AI Hallucinations: What They Are, Why They Happen, and How to Prevent Them
AI hallucinations occur when large language models and other generative AI tools produce outputs that contain factually incorrect, misleading, or entirely fabricated AI content while presenting it with apparent confidence. Unlike human hallucinations, these aren’t perceptual errors—they’re instances where AI models generate plausible-sounding content that doesn’t correspond to reality, from made-up citations to nonexistent historical events.
Understanding and preventing AI hallucination has become critical as these AI agents integrate deeper into business workflows, research processes, and decision-making systems.
What This Guide Covers
This comprehensive guide explains the technical mechanisms behind AI hallucinations, demonstrates why they occur in large language models and generative AI tools, and provides practical prompt engineering strategies—such as how to write effective prompts and use effective context engineering—to minimize them. We’ll cover real-world examples, testing approaches, and advanced context engineering techniques you can implement immediately.
Who This Is For
This guide is designed for AI researchers, developers, business users, and anyone working with generative AI tools like ChatGPT, Claude, or GPT-4. Whether you’re implementing AI systems in healthcare, legal, or financial contexts, or simply want to improve your prompting effectiveness, you’ll find actionable strategies to reduce hallucination risks.
Why This Matters
AI hallucinations can cause serious real-world harm across industries—from medical misdiagnoses to fabricated legal precedents to false financial analysis. As AI generated content becomes more sophisticated and harder to distinguish from factual information, understanding how to prompt AI models effectively becomes essential for maintaining accuracy and trust.
What You’ll Learn:
-
Definition and classification of AI hallucinations across different AI systems
-
Root causes in language models including training data limitations and architectural constraints
-
Prompt engineering techniques to provide relevant context and reduce fabrication
-
Advanced validation approaches using external data and iterative development
-
Industry best practices for AI governance and hallucination prevention


Understanding AI Hallucinations in Artificial Intelligence Systems
AI hallucinations represent instances where generative AI models create plausible-sounding but factually incorrect or ungrounded information. Unlike human hallucinations involving false perceptions, AI hallucination describes the phenomenon where artificial intelligence systems fabricate content—generating responses that sound authoritative but contain errors, contradictions, or complete fabrications.
This concept matters critically for anyone using AI tools in professional contexts because these systems can produce misleading outputs with the same confidence and coherence as accurate information. The challenge isn’t that AI models occasionally make mistakes—it’s that they present fabricated content as fact, making errors difficult to detect without external verification.
Types of AI Hallucinations and Possible Outcomes
Intrinsic hallucinations produce outputs that directly contradict the source material, training data, or conversation history. When you provide a document to an AI model and it generates a summary containing information not present in that document, you’re witnessing intrinsic hallucination. These errors can be verified by comparing the AI generated content against the original input data.
Extrinsic hallucinations involve AI models creating fictional content that cannot be verified from available sources—fabricated research papers, invented historical events, or made-up statistics. These prove particularly dangerous because they require external fact-checking to identify, and the fabricated content often appears plausible within the response context.
This connects to the main concept because both types stem from similar underlying model limitations: AI systems prioritize generating coherent, contextually appropriate responses over factual accuracy, leading to confident-sounding fabrication when sufficient information isn’t available.
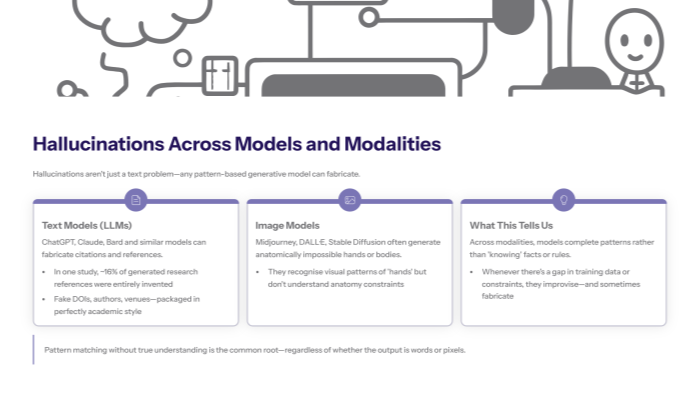
Hallucinations Across Different AI Models and Agents
Text generation models like ChatGPT, Claude, and Bard commonly fabricate citations, create false statistics, and invent historical events. In one documented case, ChatGPT generated 178 research references for academic proposals, with approximately 16% being entirely fabricated—complete with fake DOIs and nonexistent author names.
Image generation tools including Midjourney, DALL-E, and Stable Diffusion consistently produce anatomical impossibilities, such as humans with incorrect numbers of fingers, because these AI models recognize pixel patterns associated with hands but lack conceptual understanding of human anatomy constraints.
Building on the previous concept of pattern-based fabrication, these cross-modal examples demonstrate how AI systems across different domains—text, images, and audio—hallucinate when their pattern-matching approaches encounter gaps in training data or architectural limitations that prevent true conceptual understanding.
Transition: Understanding what AI hallucinations look like across different AI agents and generative AI tools provides the foundation for examining why these fabrications occur so consistently in large language models.


Why AI Hallucinations Happen in Large Language Models and AI Systems
The technical causes behind AI hallucinations in language models stem from converging factors at multiple levels—from training data quality to fundamental architectural constraints that prioritize fluency over factual accuracy.
Training Data Limitations and Their Effect on Possible Outcomes
Insufficient training data in specialized domains leaves knowledge gaps that AI models fill with fabricated information rather than acknowledging uncertainty. When generative AI models encounter queries about niche topics, recent events, or specialized fields where their training data was sparse, they often generate plausible-sounding but incorrect responses to maintain conversational flow.
Biased or inaccurate training data propagates systematic errors throughout the model’s responses. If internet data used for training contains misinformation, conspiracy theories, or outdated information, large language models incorporate these patterns and reproduce them confidently in user interactions. The Harvard Business Review noted that models trained primarily on web pages inevitably absorb the biases and inaccuracies present in that source material. Learn more about the impact of low-quality data on AI performance .
This connects to AI hallucination because language models don’t distinguish between accurate and inaccurate patterns in their training data—they simply learn to reproduce whatever linguistic patterns appear frequently, regardless of factual correctness.
Model Architecture Constraints and Adversarial Attacks
Transformer attention mechanisms and context windows create fundamental limitations in how AI models process information. Current language models can only consider a limited amount of previous context when generating each next word, meaning they may lose track of important context or constraints established earlier in a conversation.
Probabilistic text generation prioritizes linguistic fluency and contextual appropriateness over factual verification. AI models generate each response by predicting the most statistically likely next word based on patterns in training data , not by consulting external information sources or verifying claims against reality.
Unlike traditional information systems that retrieve relevant information from databases, generative AI models rely entirely on patterns memorized during training, creating inherent vulnerabilities when those patterns don’t align with current factual reality.
Overfitting, Generalization Problems, and Simple Patterns
Pattern memorization rather than conceptual understanding leads AI models to confidently reproduce training examples even when adapting them to new contexts produces factually incorrect results. When faced with complex tasks requiring reasoning beyond their training distribution, language models often generate responses that follow familiar linguistic patterns while missing essential logical constraints.
Difficulty extrapolating beyond training data boundaries causes models to fabricate information when encountering queries that require knowledge not explicitly present in their training. Rather than acknowledging uncertainty, AI systems typically generate responses that maintain conversational coherence at the expense of accuracy.
Key Points:
-
Training data quality directly impacts output reliability—gaps lead to fabrication
-
Model architecture prioritizes coherence over truth verification
-
Overfitting leads to confident but incorrect responses when extrapolating beyond training examples
Transition: Understanding these technical causes provides the foundation for developing practical prompt engineering strategies that work within these limitations to reduce hallucination frequency.

Prompt Engineering Strategies to Write Effective Prompts and Reduce AI Hallucinations
Effective prompt engineering provides AI models with relevant context, clear instructions, and structured constraints that significantly reduce hallucination likelihood while improving response accuracy and reliability.
Step-by-Step: Crafting Anti-Hallucination Prompts with the Right Words
When to use this approach: For factual queries, research tasks, professional analysis, and any high-stakes application where accuracy matters more than creative generation.
-
Provide Specific Additional Context and Constraints: Include relevant background information and explicitly state what the AI model should and shouldn’t do. Instead of “Explain climate change,” use “Based on peer-reviewed scientific literature, explain the primary causes of climate change. If you’re uncertain about any claim, please indicate that uncertainty.”
-
Request Sources and Citations: Ask the AI model to reference its information sources and acknowledge when it cannot verify claims. Example: “Please provide your analysis along with specific citations. If you cannot cite a reliable source for any claim, please note that limitation.”
-
Ask the Model to Acknowledge Uncertainty: Explicitly prompt for uncertainty quantification and acknowledgment of knowledge limits. Include phrases like “If you don’t know something, please say so” or “Rate your confidence in each major claim from 1-10.”
-
Use Structured Output Formats: Request responses in specific formats that separate facts from analysis and include metadata about confidence levels. Example: “Structure your response with: 1) Verified facts, 2) Likely but unconfirmed information, 3) Your analysis and reasoning.”
Basic vs. Anti-Hallucination Prompting and System Prompt Design
|
Feature |
Anti-Hallucination Prompt | |
|---|---|---|
|
Specificity |
“Tell me about AI ethics” |
“Based on academic research from 2020-2024, outline three major AI ethics frameworks, citing specific papers where possible” |
|
Source Requests |
None |
“Include citations for all factual claims” |
|
Uncertainty Handling |
Assumes complete knowledge |
“Acknowledge uncertainty and rate confidence” |
|
Output Structure |
Free-form response |
“Separate facts from analysis; include confidence ratings” |
Anti-hallucination prompting proves most effective when accuracy requirements outweigh creative flexibility—particularly in research, analysis, and professional decision making contexts where fabricated information creates serious risks.
Transition: These foundational techniques provide the basis for more sophisticated effective context engineering approaches that further enhance accuracy through external data integration and validation workflows.


Advanced Techniques: Effective Context Engineering and Validation for AI Agents
Effective context engineering builds on basic prompting by systematically incorporating external information sources and validation mechanisms that ground AI outputs in verifiable reality rather than relying solely on training data patterns.
Grounding with External Knowledge and System Prompt Optimization
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) techniques provide AI models with relevant information from verified databases, current documents, or authoritative sources before generating responses. Rather than asking an AI model to recall medical information from training data, provide current medical literature excerpts and ask the model to analyze based on that specific context.
Document citations and knowledge bases in prompts create explicit reference points for verification. Example template: “Based on the following document excerpts: [insert relevant passages], analyze the trend in renewable energy adoption. If your analysis extends beyond the provided information, clearly indicate where you’re drawing additional inferences.”
This approach works by giving AI systems access to external data that may be more current, accurate, or authoritative than their training data, while creating clear boundaries between supported and unsupported claims in their responses.
Multi-Step Validation Approaches and Providing Examples
Chain-of-thought prompting enhances reasoning transparency by asking AI models to show their logical steps, making errors more detectable and correctable. Instead of requesting direct answers, prompt models to “work through this problem step-by-step, showing your reasoning at each stage.”
Self-correction techniques involve asking AI models to verify their own outputs through follow-up prompts. After generating an initial response, prompt: “Review your previous answer for potential errors, contradictions, or unsupported claims. Identify any statements you cannot verify and suggest improvements.”
Cross-validation using multiple models or queries provides additional verification layers. Generate responses from different AI tools, compare outputs for consistency, and investigate discrepancies through additional research or fact-checking workflows.
Transition: While these advanced techniques significantly improve accuracy, real-world implementation often encounters specific challenges that require targeted solutions.

Common Challenges and Solutions in Managing AI Content and Possible Outcomes
Implementing anti-hallucination strategies in practice reveals consistent challenges across different use cases, each requiring specific approaches that balance accuracy requirements with operational efficiency.
Challenge 1: Model Overconfidence in Wrong Information
Solution: Use probability thresholds and confidence indicators in prompts. Rather than accepting AI responses at face value, systematically request confidence ratings and uncertainty acknowledgments. Prompt structure: “Provide your analysis followed by confidence ratings (1-10) for each major claim, and explicitly note any information you cannot verify.”
This approach works because explicit confidence requests often reveal underlying uncertainty that AI models might otherwise mask with authoritative-sounding language, helping users identify potentially unreliable information before acting on it.
Challenge 2: Subtle Factual Errors That Seem Plausible
Solution: Implement systematic fact-checking workflows and external validation. Establish verification protocols that check AI generated content against authoritative sources, particularly for specific facts, dates, statistics, and citations. Create templates that separate verifiable facts from analysis and opinion.
For high-stakes applications, develop iterative development processes where initial AI outputs undergo human review and fact-checking before final use, treating AI as a drafting tool rather than an authoritative source.
Challenge 3: Domain-Specific Hallucinations in Specialized Fields
Solution: Develop field-specific prompt templates and validation criteria. Medical applications require different safeguards than legal research or financial analysis. Create domain-specific prompts that incorporate professional standards, regulatory requirements, and field-specific verification processes.
Example for healthcare: “Analyze the following patient scenario based only on established clinical guidelines. For any recommendation, cite specific guidelines or studies. If standard protocols don’t clearly address this situation, state that explicitly and suggest appropriate specialist consultation.”
Transition: These practical solutions provide the foundation for developing comprehensive strategies that address AI hallucination risks while maximizing the benefits of AI tools in professional workflows.


Conclusion and Next Steps for AI Researchers
AI hallucinations represent an inevitable characteristic of current generative AI technology rather than a bug to be completely eliminated. However, understanding their causes and implementing systematic prompt engineering approaches can dramatically reduce their frequency and impact, making AI tools more reliable for professional and personal use.
The key insight is that effective context engineering—providing relevant information, requesting uncertainty acknowledgment, and implementing validation workflows—works within the limitations of current AI models to produce more accurate and trustworthy outputs. Success comes from treating AI systems as sophisticated pattern-matching tools that require careful input design rather than omniscient information sources.
To get started:
-
Audit current AI usage for hallucination risks: Review how you currently use AI tools and identify areas where fabricated information could cause problems
-
Implement structured prompting templates: Develop standard prompt formats for different use cases that include context provision, source requests, and uncertainty handling
-
Establish validation workflows: Create systematic processes for fact-checking AI generated content, particularly for high-stakes applications
Related Topics: As AI technology evolves, emerging areas include fine-tuning techniques for domain-specific applications , advanced AI safety research focused on truthfulness, and automated hallucination detection tools that could reduce the human effort required for validation.

Additional Resources for Writing Effective Prompts and Using System Prompts
Prompt Engineering Tools: Platforms like PromptBase, LangChain, and OpenAI’s Playground provide testing environments for developing and refining anti-hallucination prompting techniques across different AI models.
Industry Best Practices : Leading technology companies including Google, Microsoft, and OpenAI have published AI governance frameworks and responsible AI guidelines that address hallucination risks in enterprise deployments.
Academic Research: Recent papers from MIT Technology Review, Harvard Business Review, CNN Business, and the New York Times provide ongoing coverage of hallucination detection research, mitigation strategies, and regulatory approaches to AI safety in professional applications.