Generative AI Implementation: A Complete Enterprise Guide
Introduction to Gen AI and AI Technologies
Generative AI implementation represents the strategic deployment of advanced AI models and generative AI technology that can create new content, analyze data, and automate complex business processes across enterprise environments. Unlike simple AI adoption or experimentation, successful genai implementation requires comprehensive planning, technical expertise, and organizational readiness to achieve measurable business growth and business objectives.
Despite widespread interest, research shows that 95% of generative AI pilots fail to move beyond experimentation into scaled deployment. However, organizations that successfully implement these AI systems report an average return of $3.70 for every $1 invested, with productivity gains reaching 30-50% in software development and similar improvements across other knowledge-intensive domains.
What This Guide Covers
This comprehensive guide covers strategic frameworks for gen ai projects, generative ai integration approaches, technical deployment requirements, risk mitigation frameworks including ethical considerations, and success metrics for performance measurement. We focus specifically on enterprise-scale generative ai implementation rather than individual genai tools adoption or basic AI literacy.
Who This Is For
This guide is designed for business leaders, IT executives, and project managers responsible for AI development and genai adoption in enterprise environments. Whether you’re launching your first generative ai project or scaling existing AI initiatives, you’ll find actionable frameworks and proven methodologies.
Why This Matters
Generative AI implementation can drive transformational business outcomes when executed properly. The technology market is projected to reach $356 billion by 2030, with early adopters establishing significant competitive advantages through operational efficiency gains, enhanced customer experiences, and innovative content generation.
What You’ll Learn:
-
Strategic implementation framework for enterprise generative AI deployment
-
Technical requirements and architecture decisions for scalable AI systems
-
Risk management approaches for responsible AI implementation
-
Success measurement methods and key performance indicators


Understanding How Generative AI Works: AI Models and AI Algorithms
Generative AI works by utilizing advanced models such as Large Language Models (LLMs) and generative adversarial networks (GANs) to generate diverse outputs including text, images, code, and analytical insights. These AI algorithms leverage deep learning to analyze input data and training data patterns, enabling the generation of new data that mimics human creativity and intelligence.
Large Language Models like GPT-4 and Claude perform natural language processing tasks, powering content generation and interfacing with existing systems through APIs. GANs, on the other hand, specialize in image processing and synthetic data generation, playing a crucial role in visual content creation when real data is limited or sensitive.
Understanding how generative ai technology works is essential for developing ai strategies that align with business objectives and enable effective generative ai integration into enterprise workflows.
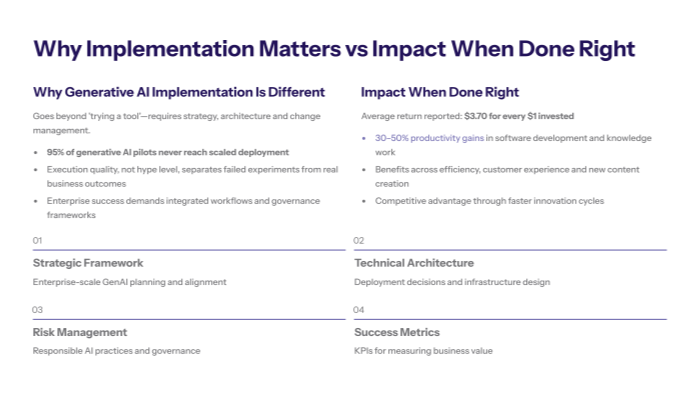
Core Technologies Behind Generative AI
-
Large Language Models (LLMs): Foundation models that handle natural language processing and content generation.
-
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): AI models that generate realistic images and synthetic data through adversarial training.
-
Advanced Models and AI Algorithms: Include transformers and variational autoencoders that contribute to new data creation and model refinement.
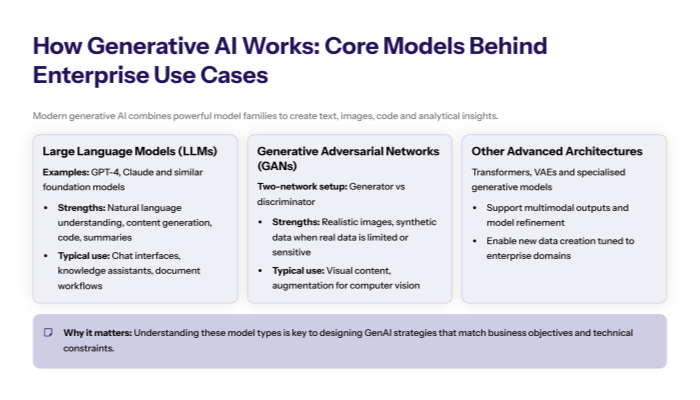

Data Collection and Data Analysis: The Foundation for GenAI Implementation
Data collection is a pivotal step in implementing genai projects. High-quality, structured data is necessary to train AI models effectively. Organizations must establish rigorous data governance frameworks and data preparation pipelines to ensure data quality and relevance.
Data analysis techniques help identify biases, gaps, and opportunities within datasets, enabling continuous improvement of AI outputs. Proper data labeling, data splitting, and handling of unstructured data contribute to the robustness of generative ai systems.
The process of utilizing generative ai depends heavily on the quality and comprehensiveness of the input data. Implementing genai without solid data collection and analysis practices risks producing unreliable or biased results.

Strategic Planning for Generative AI Implementation: Aligning with Business Objectives
Moving from foundational understanding to implementation planning requires systematic identification of high-value generative ai use cases and clear scope definition aligned with business objectives and desired outcomes.
Business Use Case Identification
Content creation and marketing automation represent high-impact applications where genai tools can produce personalized marketing content, automate social media posts, and generate product descriptions at scale. These applications enhance operational efficiency and foster business growth.
Customer service and support enhancement opportunities include automated response generation, call summarization, and intelligent routing based on customer intent analysis. Contact centers using generative ai systems for quality assurance and coaching report substantial operational efficiency improvements.
Code generation and development acceleration use cases show particularly strong returns on investment. Software development teams utilizing gen ai tools for automated code generation, testing, and documentation creation achieve 30-50% productivity gains.
Implementation Scope Definition and Key Considerations
Pilot project selection criteria should focus on measurable desired outcomes, manageable complexity, and clear success metrics. Effective pilots demonstrate specific business value while building organizational confidence and technical capabilities for broader deployment.
Scope definition involves identifying target user groups, integration requirements with existing systems, and data sources needed for model training and operation. Key considerations include scalability, security, and compliance with ethical standards.
Success metrics must align with business objectives and include both quantitative measures (productivity improvements, cost savings) and qualitative indicators (user satisfaction, content quality) that demonstrate implementation value.
Resource and Budget Planning
Technology infrastructure costs include cloud computing resources, API usage fees, and data storage requirements that scale with implementation size. Organizations using platforms like Google Cloud, AWS, or Azure for generative ai applications should budget for both development and production workloads.
Human resource requirements encompass AI teams with data scientists, machine learning engineers, and domain experts who can bridge technical capabilities with business needs. Training programs for existing staff ensure successful adoption and ongoing optimization of generative ai solutions.
Key Points:
-
Use case selection drives implementation success more than technology sophistication
-
Pilot projects should demonstrate clear ROI within 3-6 months
-
Budget planning must account for both technical infrastructure and organizational change costs


Step-by-Step Generative AI Implementation Process: From Developing AI to Full Deployment
Building on strategic planning, successful genai implementation follows a structured methodology that minimizes risk while maximizing learning and business impact.
Step 1: Data Preparation and Governance
Establish data collection protocols, implement data encryption standards, and create governance frameworks that ensure responsible AI practices while maintaining data quality for model training. This phase is crucial for utilizing generative ai effectively and preventing bias.
Step 2: Proof of Concept Development
Build and test initial AI models with limited scope, focusing on one specific use case to validate technical feasibility and business value before broader deployment. This step allows organizations to generate diverse outputs and evaluate model performance.
Step 3: Model Selection and Generative AI Integration
Choose between options like OpenAI GPT-4, Anthropic Claude, or custom foundation models based on performance requirements, data control needs, and integration complexity with existing systems. Generative ai integration into business processes is a crucial role for ensuring seamless operation and maximizing impact.
Step 4: Pilot Deployment
Roll out to limited user groups with structured feedback collection, monitoring model performance and user adoption patterns to identify optimization opportunities. This phase supports continuous improvement and helps refine genai tools based on real-world use.
Step 5: Full-Scale Implementation and Change Management
Execute enterprise-wide deployment with comprehensive monitoring, continuous improvement processes, and change management support to ensure sustained success. Change management is essential to foster user acceptance and align genai adoption with organizational culture.


Build vs Buy vs Hybrid Approaches: Choosing the Right AI Development Path
Feature |
Custom Development |
Third-Party APIs |
Hybrid Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
Implementation Timeline |
6-18 months |
1-3 months |
3-9 months |
Cost Structure |
High upfront, low ongoing |
Low upfront, high ongoing |
Moderate upfront and ongoing |
Customization Level |
Complete control |
Limited customization |
Selective customization |
Data Control |
Full control |
Vendor-dependent |
Selective control |
Maintenance Requirements |
High internal resources |
Vendor-managed |
Shared responsibility |
Organizations with sensitive data and specific requirements often benefit from hybrid approaches that combine third-party generative ai tools for general applications with custom development for critical business processes requiring specialized functionality.


Common Implementation Challenges and Solutions: Ethical Considerations and Technical Expertise
Understanding typical obstacles in generative ai implementation helps organizations proactively address issues that cause project delays or failures.
Challenge 1: Data Quality and Bias Management
Solution: Implement comprehensive data governance framework with bias detection tools and human oversight processes to ensure AI generated content meets quality standards and ethical considerations.
Data labeling processes and data splitting methodologies help maintain training data quality while regular audits identify potential bias in model outputs. Organizations should establish clear protocols for handling raw data and validating synthetic data used in model development.
Challenge 2: Integration with Legacy Systems and Generative AI Integration
Solution: Use API-first architecture and middleware solutions to connect generative ai tools with existing enterprise software, enabling seamless data flow and process automation.
Modern integration platforms facilitate connections between gen ai tools and enterprise resource planning systems, customer relationship management platforms, and other business applications without requiring major infrastructure changes. Generative ai integration is a crucial role in ensuring business continuity and operational efficiency.
Challenge 3: User Adoption and Change Management
Solution: Develop comprehensive training programs and establish AI champions across departments to drive adoption while addressing concerns about job displacement and workflow changes.
Success depends on demonstrating how generative ai systems augment rather than replace human capabilities, providing clear benefits to end users while maintaining transparency about AI decision-making processes.


Future Trends in Generative AI Technology and GenAI Projects
As generative ai technology evolves, future trends include the rise of multimodal AI models that combine text, images, audio, and video generation capabilities, further expanding the scope of genai projects.
Advancements in explainable AI and ethical AI frameworks will play a crucial role in responsible genai adoption, addressing transparency and bias mitigation challenges.
The integration of generative ai with edge computing and AI democratization through no-code platforms will make these technologies more accessible across industries.
Continuous innovation in AI algorithms and advanced models will enhance the ability to generate diverse outputs, improving personalization and operational efficiency.

Conclusion and Next Steps: Implementing GenAI for Business Growth
Successful generative ai implementation requires strategic planning, technical expertise, and organizational readiness that extends beyond technology deployment to encompass process redesign and cultural change management.
To get started:
-
Conduct Implementation Readiness Assessment: Evaluate your organization’s data infrastructure, technical capabilities, and change management readiness before selecting specific generative ai applications.
-
Identify High-Value Pilot Project: Choose a specific use case with clear success metrics, manageable scope, and strong business sponsor support to demonstrate implementation value.
-
Build Cross-Functional Implementation Team: Assemble team including business stakeholders, data scientists, IT infrastructure specialists, and change management experts to ensure comprehensive project execution.
By focusing on continuous improvement and leveraging the full capabilities of genai tools, organizations can unlock significant business growth and competitive advantage.
Related Topics: Consider exploring AI ethics frameworks, model fine-tuning methodologies, AI infrastructure best practices, and enterprise AI governance structures as your implementation progresses and requirements evolve.

