Overcoming the 8 Critical Challenges in Generative AI Implementation
Introduction to AI Technologies and Generative AI Adoption
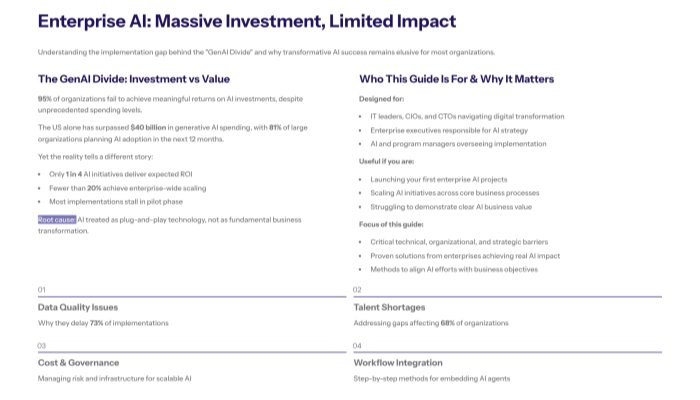
Generative AI implementation failures plague 95% of enterprise initiatives, creating massive gaps between ambitious AI visions and operational reality. Despite significant investments in AI technologies, most organizations struggle with deployment challenges that extend far beyond technical considerations, encompassing data privacy, ethical concerns, complex data sets, talent shortages, and regulatory compliance complexities, which can lead to costly data breaches if not properly managed.
Recent MIT research reveals a stark disconnect: while purchasing specialized genai tools from vendors succeeds approximately 67% of the time, internal builds of gen ai models achieve success only 33% as often, highlighting fundamental misunderstandings about generative artificial intelligence deployment complexity and the need to implement mechanisms that ensure effective integration and governance.
What This Guide Covers
This guide examines the eight critical implementation barriers that derail generative AI initiatives, from technical infrastructure gaps to organizational resistance. We focus on practical mitigation strategies and proven deployment frameworks rather than theoretical AI concepts or basic technology overviews, providing an in depth analysis of challenges and solutions.
Who This Is For
This guide is designed for enterprise leaders, IT directors, and digital transformation teams planning or struggling with generative AI adoption. Whether you’re initiating your first gen AI project or scaling existing pilots, you’ll find actionable strategies to navigate implementation roadblocks and build customer trust through responsible AI use.
Why This Matters
Implementation failures result in substantial financial losses, missed competitive advantages, and organizational resistance to future AI adoption. The 95% failure rate represents billions in wasted investment and unrealized operational efficiency gains across industries from health care to financial services, potentially resulting in reputational damage and loss of proprietary information.
What You’ll Learn:
-
Eight critical implementation barriers that cause project failures
-
Proven risk assessment framework for pre-deployment planning
-
Technical architecture requirements for successful deployment, including modular architectures and agentic AI approaches
-
Step-by-step mitigation strategies for common obstacles

Understanding Artificial Intelligence and Complex Data Sets in Generative AI Implementation
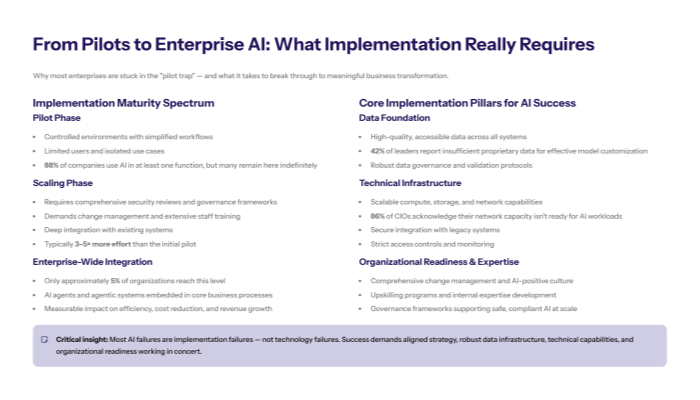
Generative AI implementation encompasses the complete enterprise-scale deployment of AI systems beyond basic adoption, requiring integration with existing business models, data infrastructure, and organizational workflows.
Enterprise-scale deployment introduces complexities that don’t exist in consumer applications or pilot projects. Generic genai technology like large language models excel for individual users because of their inherent flexibility, but they stall in enterprise environments because they don’t learn from or adapt to organizational workflows and specific business processes, especially those with stringent compliance requirements.
This fundamental mismatch between consumer-grade genai tools and enterprise requirements creates what researchers call the “GenAI Divide”—a disconnect between what organizations expect from gen ai capabilities and what they actually achieve in practice.
Pre-Implementation Planning Barriers: Ethical Considerations and Building Trust
Lack of clear business case definition and ROI measurement creates the foundation for implementation failure. Organizations frequently launch gen ai initiatives without establishing measurable success metrics or understanding total cost of ownership, including infrastructure, human resources, maintenance, and ongoing AI development costs.
Insufficient stakeholder alignment across departments compounds planning challenges. When business leaders envision generative AI tools solving specific problems while IT teams struggle with technical implementation realities, infrastructure constraints, or data quality issues, projects encounter resistance and resource conflicts.
This connects to implementation challenges because planning failures cascade into execution problems. Without clear objectives and unified stakeholder support, organizations lack the strategic focus necessary to navigate technical complexities, ethical implications, and change management requirements.
Resource Requirements and Infrastructure Gaps for AI Models
Computing infrastructure inadequacy for AI workloads represents a critical barrier. Generative AI systems require substantial computational resources for both training and inference, often exceeding existing enterprise infrastructure capabilities. Organizations must invest in specialized hardware, cloud computing resources, or hybrid architectures to support AI applications effectively.
Data architecture limitations in legacy systems create additional obstacles. Modern AI systems require vector databases for managing embeddings, semantic frameworks like knowledge graphs to establish context and relationships, and sophisticated data integration capabilities that many enterprises lack.
Building on planning barriers, resource gaps compound planning issues because inadequate infrastructure assessment during planning phases leads to cost overruns, timeline delays, and performance degradation during deployment. Organizations that underestimate infrastructure requirements face substantially higher failure risks.
Transition: While foundational challenges establish the context for implementation difficulties, specific technical barriers create the most immediate obstacles during deployment.

Technical Implementation Barriers in Content Creation and Data Synthesis
Moving from planning considerations to actual deployment, organizations encounter complex technical challenges that require specialized expertise and robust architectural approaches to overcome successfully.
Data Quality, Data Auditing, and Integration Challenges with Synthetic Data and Real World Data
Unstructured data preprocessing complexities plague most enterprise implementations. Generative AI models require exceptionally large volumes of diverse datasets and high-quality training data, but organizations frequently lack the data cleaning capabilities, standardization processes, or governance frameworks to meet these requirements. AI systems have fundamentally different data standardization and vectorization requirements compared to traditional analytics systems.
Data silos preventing unified model training create additional integration obstacles. Legacy enterprise systems often store complex data sets across disconnected databases, applications, and platforms without unified access mechanisms. This fragmentation prevents organizations from leveraging complete data sets for AI model training and reduces the effectiveness of gen ai outputs.
Privacy and compliance constraints limiting data access compound integration challenges. Regulatory frameworks like GDPR impose strict requirements for handling personally identifiable information, sensitive information, and potential risks like identity theft, while industry-specific regulations in health care and financial services create additional compliance burdens that directly impact data engineering work.
Model Deployment and Integration Complexity in Modular Architectures
API integration challenges with existing enterprise systems create significant deployment friction. Connecting generative AI models to heterogeneous IT environments requires sophisticated middleware solutions, custom development work, and ongoing maintenance that many organizations underestimate during planning phases.
Real-time inference performance bottlenecks affect user experience and system reliability. Large language models must process input data and generate responses within acceptable timeframes, but computational demands often exceed infrastructure capabilities, resulting in latency problems that limit practical adoption.
Version control and model governance difficulties emerge as organizations scale beyond pilot projects. Managing model updates, monitoring performance drift, and maintaining audit trails for regulatory compliance requires governance frameworks that many enterprises lack.
Scalability and Performance Issues Affecting Business Models and Revenue Growth
Computational cost escalation at enterprise scale creates ongoing financial challenges. While pilot projects may operate within reasonable cost parameters, scaling to hundreds or thousands of concurrent users dramatically increases infrastructure expenses and operational complexity.
Latency problems in production environments limit real-world applicability. Generative AI applications must deliver responses quickly enough to support business processes, but computational requirements often conflict with performance expectations, particularly for complex queries or large-scale content generation tasks.
Load balancing challenges for concurrent users require sophisticated infrastructure management. As organizations expand gen ai adoption across departments and user groups, maintaining consistent performance becomes increasingly difficult without proper architectural planning.
Key Points:
-
Infrastructure requirements exceed typical enterprise capabilities
-
Data integration complexity multiplies with existing system heterogeneity
-
Performance optimization requires specialized architectural expertise
Transition: Understanding technical barriers provides the foundation for systematic risk assessment and mitigation planning.


Strategic Risk Assessment and Mitigation for Responsible Use and Ethical Issues
Building on technical barrier identification, organizations need structured approaches to evaluate implementation risks and develop targeted mitigation strategies before initiating deployment projects.
Step-by-Step: Implementation Risk Assessment with Emphasis on Ethical Concerns and Data Privacy
When to use this: Before initiating any generative AI deployment project, particularly for organizations without prior enterprise AI experience.
-
Conduct technical infrastructure audit and capability assessment: Evaluate existing computing resources, data architecture maturity, and integration capabilities against gen ai requirements. Include assessment of vector database needs, API management capabilities, and real-time processing capacity.
-
Map data sources and identify integration complexity: Document all relevant data sets, assess data quality and accessibility, evaluate regulatory constraints, and identify preprocessing requirements. Include analysis of data silos, format standardization needs, and privacy compliance requirements.
-
Evaluate regulatory compliance requirements by jurisdiction: Assess applicable regulations including data privacy laws, industry-specific requirements, and ethical frameworks. Include analysis of audit trail requirements, data governance obligations, and potential legal ramifications related to data breaches or misuse of proprietary information.
-
Assess team skills gap and training needs: Evaluate current team capabilities against required expertise including data science, machine learning engineering, domain knowledge, and AI governance. Include assessment of external consulting needs and ongoing training requirements.
Comparison: Build vs Buy vs Partner Implementation Approaches in AI Adoption
Approach |
Cost |
Time to Market |
Control |
Expertise Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Build In-House |
High upfront, ongoing maintenance |
12-24 months |
Complete control |
Significant AI/ML expertise |
Purchase Enterprise Solutions |
Medium subscription fees |
3-6 months |
Limited customization |
Integration expertise |
Partner with AI Vendors |
Variable, often success-based |
6-12 months |
Shared control |
Business domain expertise |
Research indicates that purchasing specialized genai tools from vendors succeeds approximately 67% of the time, while internal builds achieve success only one-third as often. Organizations should consider vendor partnerships when lacking internal AI expertise or requiring rapid deployment timelines. |
Transition: Even with thorough risk assessment, specific implementation challenges require targeted solution strategies.


Common Challenges and Solutions for Fostering Trust and Managing Ethical Implications
Based on enterprise implementation patterns, three critical challenges consistently emerge across organizations and industries, requiring specific mitigation strategies for successful deployment.
Challenge 1: AI Skills Gap and Talent Shortage Impacting Human Resources and Decision Making Processes
Inadequate generative AI expertise affects 42% of organizations according to IBM research, creating bottlenecks in model development, deployment, and maintenance capabilities.
Solution: Implement a hybrid approach combining internal upskilling with external consulting partnerships. Establish structured training programs for existing technical staff while engaging specialized AI consultants for initial deployment phases and knowledge transfer.
Organizations should prioritize hiring data scientists capable of developing AI models, machine learning engineers who can deploy AI systems, and domain experts who understand industry-specific requirements while building internal capabilities through continuous learning programs.
Challenge 2: Regulatory Compliance and Governance Addressing Ethical Issues and Potential Risks
Regulatory considerations create complex compliance requirements that vary by jurisdiction and industry, with particular complexity around data privacy, ethical AI use, and audit trail maintenance.
Solution: Establish an AI ethics committee and comprehensive compliance framework before deployment. Implement robust data governance policies, audit trail mechanisms, and regular compliance reviews to ensure ongoing regulatory adherence.
Include development of ethical frameworks for responsible AI use, implementation of bias detection and mitigation strategies, and establishment of clear guidelines for AI generated content usage and intellectual property protection.
Challenge 3: Cost Management and ROI Uncertainty Affecting Business Models and Revenue Growth
Calculating return on investment for gen ai initiatives proves particularly complex because potential benefits may span extended timeframes, involve operational efficiency improvements difficult to quantify, or manifest across departments in ways challenging to attribute directly to AI implementation.
Solution: Implement phased deployment with clear success metrics at each stage. Start with small, high-impact pilot projects to demonstrate value and build business cases for further investment, utilizing value of investment (VOI) frameworks to prioritize projects offering the greatest strategic and financial benefits.
Establish robust cost monitoring frameworks that track infrastructure expenses, personnel costs, and indirect benefits while maintaining realistic expectations about timeline for measurable returns.
Transition: Systematic approaches to these common challenges provide the foundation for sustainable generative AI adoption.


Conclusion and Next Steps: Building Trust and Driving Responsible AI Adoption
Successful generative AI implementation requires systematic approaches that address technical, organizational, and strategic challenges simultaneously. The 95% failure rate reflects not inadequate AI technologies, but rather insufficient attention to implementation complexity and organizational readiness.
Organizations that acknowledge these eight critical barriers and implement structured mitigation strategies achieve substantially better outcomes than those attempting ad hoc deployment approaches. Building trust through responsible AI practices, fostering digital literacy across teams, and maintaining focus on measurable business value creates the foundation for sustainable AI adoption.

To get started:
-
Complete immediate risk assessment: Use the four-step framework to evaluate your organization’s readiness and identify critical gaps
-
Conduct stakeholder alignment meeting: Bring together business leaders, IT teams, and compliance stakeholders to establish unified objectives and success metrics. In one example, a managing director of a leading enterprise emphasized the importance of cross-functional collaboration to ensure success.
-
Define focused pilot project: Select a specific, measurable use case that demonstrates value while building organizational AI capabilities, potentially resulting in higher adoption rates and operational efficiencies.
Related Topics: Consider exploring AI development services for transforming your business solutions, AI governance frameworks for ongoing compliance management, change management strategies for organizational adoption, and continuous optimization approaches for scaling successful pilots across enterprise operations.

