What Is Prompt Engineering? Simple Explanation for Non-Engineers
If you’ve ever used AI tools like ChatGPT or other generative AI assistants, you’ve probably noticed something strange:
Sometimes the answers are amazing.
Other times they’re vague, off-topic, or just plain wrong.
That’s where prompt engineering comes in. It’s the skill of crafting clear, effective instructions (called “prompts” ) that guide an AI model to give you the best possible responses.
In this article, you’ll learn what prompt engineering is , how language models actually work, and how you can start using prompt engineering techniques right away — no technical background required.


Why We Need Prompt Engineering in Everyday Generative AI Use?
When people first try gen AI tools, the expectation is often:
“I’ll just type what I want, and the AI will magically understand.”
In reality, models like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and others are generative AI systems that respond based on patterns in data. If your user prompts are vague, the results will be vague too.
Prompt engineering is important because it helps you:
-
Turn a messy idea into a specific output
-
Get more accurate responses from the same AI model
-
Handle more complex tasks (like analysis or planning) with less frustration
-
Produce relevant responses that match your desired outcomes
You’re not just “chatting with a robot.” You’re learning to direct a powerful system with carefully chosen words.


What Is Prompt Engineering? (Core Definition)
A Simple Definition for Non-Engineers
At its core, prompt engineering is the process of designing and refining the instructions you give to an AI system so that it produces useful, accurate, and relevant output.
A prompt might look like a question, but it’s more than that. It’s a call to action that tells the AI what to do , how to do it , and often how the final answer should look .
Put simply:
Prompt engineering = the skill of asking AI in the right way so it can generate the answers you actually need.
How Experts Define Prompt Engineering?
Major organizations describe it in similar terms:
-
IBM describes prompt engineering as structuring instructions so generative AI models can produce better, more aligned outputs.
-
OpenAI defines it as writing effective instructions so a model consistently generates content that meets your requirements.
-
Wikipedia calls it the process of crafting prompts to get better outputs from generative artificial intelligence models.
All of these share the same idea: you shape the AI’s behavior through prompt design.

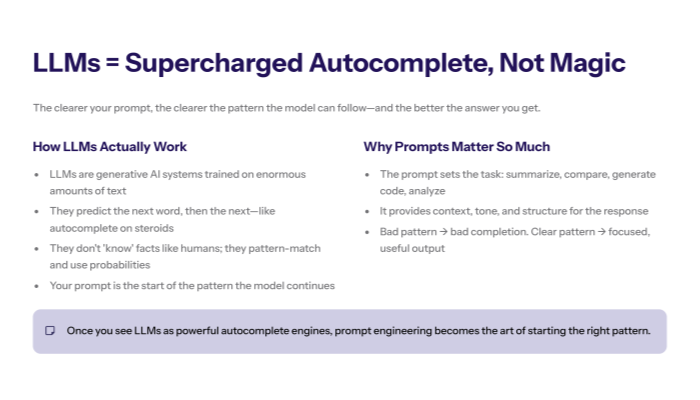
How Modern AI Models Work (Supercharged Autocomplete, Not Magic)
Large Language Models as Generative AI Systems
Modern tools like ChatGPT are built on large language models (LLMs) — a kind of artificial intelligence that has been trained on enormous amounts of text.
These models power many generative AI tools that can:
-
Answer questions
-
Write a news article
-
Generate code
-
Suggest improvements to existing code
-
Summarize uploaded documents
-
Even help with images and structured data in some workflows
The “Autocomplete” Mental Model for Language Models
The easiest way to think about an LLM is as supercharged autocomplete :
-
You start typing a sentence.
-
The model predicts the most commonly reached conclusion — the next word, then the next, and so on.
The AI doesn’t “know” things in the human sense. It’s performing complex reasoning by pattern-matching and probability, not by understanding like human intelligence does.
Because everything is based on prediction, your prompt is the start of the pattern .
Bad pattern → bad completion.
Clear pattern →
relevant output
that feels smart.
Why the Prompt Shapes the Final Answer?
Since the model predicts what comes next based on your text and its training, the prompt:
-
Sets the task (“summarize”, “compare”, “generate code”, “analyze”)
-
Provides context (what information to use)
-
Hints at the expected response (tone, structure, length)
If you give the model a vague “user’s query”, it will give you a vague guess.
If you give it
precise instructions
, it can
produce optimal outputs
.

Prompts Are Programs in Natural Language
A Prompt as a Call to Action for an AI Model
In traditional software, a programming language like Python gives instructions to a computer.
With AI prompt engineering , you’re doing something similar — except your “language” is natural language (English, Spanish, etc.).
A prompt isn’t just:
“Tell me about dogs.”
It can be a direct instruction like:
“You are a friendly veterinarian.
Explain in two short paragraphs why dogs make great pets for families with kids. Use simple language and avoid medical jargon.”
This prompt specifies: 10 essential artificial intelligence books to read .
-
Role of the AI model (veterinarian)
-
Task (explain why dogs make great pets)
-
Desired output (two short paragraphs, simple language)
That’s prompt design — you’re programming with words.
Prompt Design vs Traditional Programming Language
You don’t need to write code to practice effective prompt engineering .
However, thinking like a programmer helps:
-
You define inputs (context, data, constraints)
-
You specify the process (steps, intermediate steps )
-
You describe the final answer you want
The difference is that instead of code, you use sentences and examples .

Core Prompt Engineering Techniques (Zero-Shot, Few-Shot, Chain-of-Thought)
To get better at prompt engineering skills , it helps to know a few simple prompting techniques .
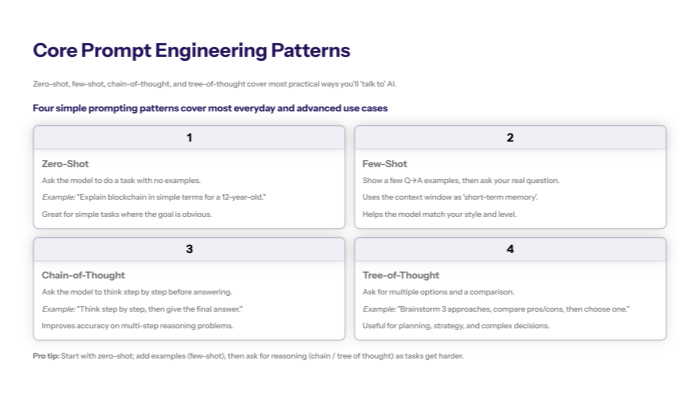
Zero-Shot Prompting – When You Give No Examples
Zero shot prompting means you ask the AI to perform a task without providing any training examples .
Example:
“Explain blockchain in simple terms for a 12-year-old.”
This can work well for simple tasks, but for complex tasks , the model may guess what you want and miss your desired output .
Few-Shot Prompting – Learning from a Few Examples
Few shot prompting means you show the AI a few examples of what you want before asking it to respond.
You’re using the model’s context window (its short-term memory) to teach it.
Example (few examples embedded in the prompt):
“Here are some examples of how to respond:
Q: What is machine learning?
A: Machine learning is a way for computers to learn patterns from data instead of being programmed with fixed rules.Q: What is cloud computing?
A: Cloud computing lets you use computing power and storage over the internet instead of on your own device.Now follow the same style:
Q: What is prompt engineering?”
This gives the AI a pattern so it can generate desired outputs in a consistent voice.
Chain-of-Thought Prompting – Step-by-Step Reasoning
Chain of thought prompting asks the model to show its reasoning step by step before giving a final answer.
Example:
“The cafeteria had 23 apples. They used 20 to make lunch and bought 6 more.
Think step by step and then tell me how many apples they have now.”
With chain of thought prompting , the model might respond:
-
They started with 23 apples.
-
They used 20, leaving 3.
-
They bought 6 more, so 3 + 6 = 9.
-
Final answer: 9 apples.
By asking for reasoning, you improve the model’s complex reasoning and often get more accurate responses on multi-step problems.
Tree-of-Thought Prompting and Complex Tasks
A more advanced idea is tree of thought prompting , where the AI explores multiple reasoning paths instead of just one.
For example, you might say:
“Brainstorm three different approaches to solving this problem.
Evaluate each one, explain pros and cons, and then choose the most commonly reached conclusion and justify it.”
This kind of thought prompting is especially helpful for planning, strategy, and other complex tasks .

Before vs After – Prompt Examples that Generate Desired Outputs
Let’s look at some practical prompt engineering techniques with specific examples .
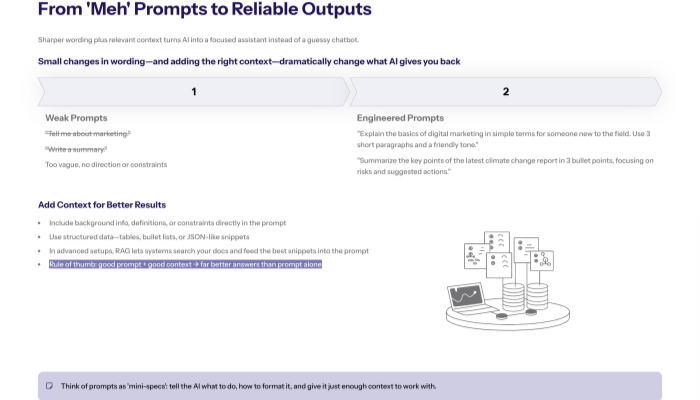
Example Table – Weak vs Engineered Prompts
Here’s a quick comparison:
|
Task |
Weak Prompt |
Engineered Prompt (Better Prompt Design) |
|---|---|---|
|
Explain marketing |
“Tell me about marketing.” |
“Explain the basics of digital marketing in simple terms for someone new to the field. Use 3 short paragraphs and a friendly tone.” |
|
Summarize a report |
“Write a summary.” |
“Summarize the key points of the latest climate change report in 3 bullet points , focusing on risks and suggested actions.” |
|
Generate code |
“Write Python code.” |
“You are a senior Python developer. Write a function that takes a list of numbers and returns the average. Include code snippets only.” |
|
Improve existing text |
If you're unsure how to fix this, consider reading this clear and concise guide for beginners on prompts in LLMs . |
“You are an editor. Suggest improvements to the following email for clarity and professionalism. Keep the meaning the same.” |
Notice how the improved prompts:
-
Include direct instruction
-
Specify the desired output (tone, length, structure)
-
Help the model produce relevant output with fewer retries
Using Format, Tone, and Constraints for More Accurate Responses
You can often get more accurate responses by telling the AI exactly how to reply; for a step-by-step guide on how to set up and use your own local AI server, check out Local AI Server A Step by Step Guide to Setup and Use :
-
Number of bullet points
-
Word count range
-
Tone (formal, casual, neutral)
-
Audience (beginner, expert, child, executive)
These details act like parameters in a program. The clearer you are, the easier it is for the AI to match your expected response .

Adding Context and Structured Data for Better Results
Context Windows, Uploaded Documents, and Additional Context
Every AI model has a context window — a limit to how much information it can consider at once.
To handle complex tasks , you can add:
-
Additional context (background info, definitions, constraints)
-
Structured data (tables, bullet lists, JSON-like formats)
-
Uploaded documents (reports, notes, transcripts, depending on the tool)
The more relevant and clear the context, the easier it is for the model’s ability to:
-
Understand the situation
-
Connect your question with the right details
-
Produce relevant responses instead of hallucinations
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) in Simple Terms
In more advanced setups, systems use retrieval augmented generation . That simply means:
-
The system searches your documents or a database.
-
It pulls in specific examples or snippets.
-
It feeds them into the model’s context window.
-
The model uses that context to generate desired outputs .
Even if you’re not building these systems yourself, it’s helpful to know that good prompts + good context = better results.

Prompt Engineering Use Cases in Generative AI Tools
Prompt engineering isn’t just for writing essays. It powers many prompt engineering use cases across different generative AI models .
Writing and Summarizing a News Article
You can:
-
Draft a news article from bullet points
-
Summarize a long report into key takeaways
-
Turn messy notes into a structured blog post
With the right prompt design, the AI can produce optimal outputs aligned with your audience and format.
Coding Tasks, Existing Code, and Code Snippets
For coding tasks , AI can:
-
Generate code from a description
-
Refactor existing code
-
Provide code snippets to solve specific problems
You just need to be explicit:
“You are a backend engineer. Using Python, generate code that connects to a PostgreSQL database and runs a simple SELECT query. Include comments.”
Generate Images, Generate Code, and More
With multimodal generative AI tools , prompts can:
-
Generate images (“a high-quality photo of a red sports car in the rain”)
-
Generate code from a natural language description
-
Walk through intermediate steps to solve a problem
All of these rely on the same foundation: clear, structured prompts .

Why Prompt Engineering Is Important for Non-Engineers?
Critical Thinking, Human Intelligence, and Responsible AI Use
Good prompt engineering forces you to practice critical thinking :
-
What do I really want?
-
What counts as a good answer?
-
What context is essential?
This kind of thinking is key to responsible AI use. You’re not just accepting any output — you’re designing inputs and checking the model’s responses.
How Prompt Engineering Skills Improve Everyday Work?
Prompt engineering is important because it helps you:
-
Work faster (less time fixing bad answers)
-
Communicate better with generative AI tools
-
Turn vague ideas into clear, action-ready text or plans
Some companies are even hiring prompt engineers — people who specialize in designing prompts for generative AI systems across marketing, software development, and education.
Even if you never apply for prompt engineering jobs , these skills make you more effective in almost any role.

Careers and Hiring Prompt Engineers
Prompt Engineering Jobs and Evolving Roles in Gen AI
Reports from industry and media note that prompt engineering jobs emerged quickly as companies realized they needed people who know how to “talk to AI” effectively.
Typical responsibilities include:
-
Designing prompts for generative AI models
-
Testing and optimizing prompts for relevant output
-
Working with teams to integrate AI into workflows
While some analysts argue the role may evolve as models better understand language, the underlying skill of clear prompt design remains valuable.
What Employers Look for When Hiring Prompt Engineers
According to sources like IBM and others, useful skills include:
-
Strong communication and writing skills
-
Understanding of AI models and their limits
-
Some familiarity with programming languages and APIs
-
Ability to balance creativity with responsible AI practices
In many ways, it’s less about “knowing secret tricks” and more about being good at explaining complex ideas clearly .

How to Start Learning Prompt Engineering Today
You don’t need a degree in AI to learn prompt engineering . Start with a simple practice loop.
A Simple Checklist for Effective Prompt Engineering
Before you send a prompt, quickly check:
-
Role – Who should the AI pretend to be?
-
Task – What exactly should it do? (summarize, analyze, generate, compare, etc.)
-
Context – What background or data does it need?
-
Format – How should the answer be structured? (bullets, table, steps, word count)
-
Constraints – Any rules? (tone, audience, avoid jargon)
This checklist makes your user prompts more like little programs that the model can execute.
Practising Prompting Techniques with Specific Examples
Pick one tool (like ChatGPT) and practice:
-
Zero shot prompting – ask for something simple
-
Few shot prompting – add a few examples first
-
Chain of thought prompting – ask it to think step by step
-
Tree of thought prompting – ask for multiple options and a comparison
For example:
“You are a tutor helping a beginner understand prompt engineering.
Use chain of thought prompting : think step by step about how to explain it, then give a clear explanation in 3 paragraphs.”
Then tweak the prompt:
-
Add more additional context
-
Change the desired output format
-
Adjust the prompt design to handle more complex tasks
This iterative refinement approach is exactly what OpenAI and others recommend as a prompt engineering best practice .

Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Overloading the Model vs Precise Instructions
A common mistake is writing a huge, messy prompt that tries to do everything at once.
Instead:
-
Keep each prompt focused on a specific output
-
For very complex tasks, break them into smaller intermediate steps
-
Use providing examples instead of long, abstract explanations
When the Model’s Responses Miss the Point
If the model’s responses are off:
-
Check if your instructions are actually clear
-
Ask yourself: “Would a human understand exactly what I want from this?”
-
Try adding few examples or more structured data (lists, tables)
-
If needed, explicitly ask the AI to suggest improvements to your prompt first
Often, fixing the prompt fixes the output.

Summary: Prompt Engineering as Clear Thinking, Written Down
So, what is prompt engineering?
It’s the practice of designing, testing, and refining prompts so that generative AI can help you more effectively.
Instead of treating AI as magic, you:
-
Understand that LLMs are advanced autocomplete
-
Treat prompts as programs written in natural language
-
Use prompt engineering techniques like zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought
-
Apply critical thinking to get better, more relevant responses
You don’t need to become a full-time “prompt engineer” to benefit from this.
A bit of
effective prompt engineering
turns AI from a confusing toy into a reliable assistant.

A Starter Prompt You Can Try Right Now
Copy this into your favorite AI tool:
“Explain what prompt engineering is in simple terms for someone who has never heard of it.
Use 2–3 short paragraphs, avoid technical jargon, and include one example comparing a weak prompt and a better prompt.”
Watch the model’s ability to respond improve as you start giving it better instructions.
That’s prompt engineering in action — and you’ve just taken your first real step in learning it.

