AI Governance Implementation: Building Effective Governance Frameworks in 2026
Introduction to AI Governance and AI Systems
AI governance implementation is the systematic process of translating abstract governance principles into concrete policies, controls, and workflows that shape how AI systems operate, including their development, deployment, and continuous monitoring throughout their lifecycle. Unlike theoretical frameworks that outline what organizations should do, AI governance implementation focuses on the practical steps of building operational governance structures that ensure responsible AI development while meeting regulatory compliance requirements such as those mandated by the AI Act.
Recent studies show that while 79% of business leaders view artificial intelligence technologies as critical to their competitive advantage, 60% lack clear implementation plans for governing their AI initiatives effectively.
What This Guide Covers
This guide provides a step-by-step methodology for implementing AI governance frameworks and governance practices, from initial planning through operational deployment. We cover framework development strategies, policy integration processes, and practical solutions to common implementation challenges. This guide does NOT include theoretical AI ethics discussions or vendor-specific tool comparisons.
Who This Is For
This guide is designed for Chief Data Officers, compliance managers, IT leaders, and executives responsible for AI governance in their organizations. Whether you’re building AI governance from scratch in a rapidly scaling startup or updating existing governance frameworks to comply with new AI regulations like the EU AI Act, you’ll find actionable implementation strategies and risk mitigation approaches.
Why AI Governance Is Important
With EU AI Act enforcement beginning February 2025, organizations face regulatory penalties up to 7% of global revenue for non-compliance with AI governance requirements. Beyond compliance, effective AI governance reduces the risk of bias incidents, AI system failures, unintended consequences, and reputational damage that can cost organizations millions in remediation and lost business value. Implementing responsible AI governance ensures AI outcomes are trustworthy and aligned with organizational values and ethical standards.
What You’ll Learn:
-
Foundation elements and core principles for implementing robust AI governance frameworks
-
Framework development and policy integration processes aligned with regulatory compliance and ethical guidelines
-
Step-by-step implementation methodology with realistic timelines and resource allocation
-
Evidence-based solutions to common implementation roadblocks and organizational challenges


Understanding the AI Governance Process in AI Development
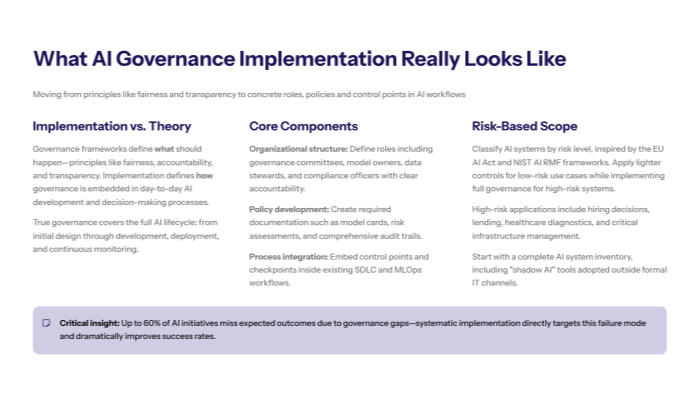
AI governance implementation encompasses the concrete, end-to-end AI governance process by which organizations translate abstract AI governance principles—such as fairness, accountability, transparency, and safety—into operating models, controls, workflows, and technologies that reliably shape AI development, model development, and AI operations.
This implementation process differs fundamentally from developing governance frameworks or policies. While frameworks define what should be done, implementation focuses on how governance actually gets embedded into daily AI development workflows and organizational decision-making processes.
Research indicates that 60% of AI initiatives fail to deliver expected AI outcomes due to governance gaps, making systematic implementation crucial for AI success.
Core Principles and Key Components of AI Governance Implementation
AI governance encompasses several core principles that guide responsible AI governance initiatives, including ethical development, data privacy, data integrity, and adherence to legal and ethical boundaries. These principles form the operational backbone of effective governance:
Organizational Structure and Role Definitions: Clear accountability through designated AI governance committees, model owners, data stewards, and compliance officers who have specific responsibilities for AI system oversight throughout the AI lifecycle.
Policy Development and Documentation Requirements: Comprehensive policies that specify how AI models must be developed, validated, deployed, and monitored, along with standardized documentation templates for model cards, risk assessments, and audit trails.
Process Integration and Control Points: Embedded governance checkpoints in existing workflows that ensure AI governance practices are enforced consistently across all AI initiatives and AI development processes.
These components connect to create a comprehensive governance framework because each addresses a different dimension of implementation: organizational accountability, operational guidance, and process enforcement.
Defining Scope and Managing AI Specific Risks
Successful AI governance implementation requires clear boundaries around which AI systems require governance oversight and what level of control is appropriate for different risk categories.
Risk-Based Classification Approach: Following the EU AI Act and NIST AI Risk Management Framework, organizations implement tiered governance based on AI system risk levels—from minimal oversight for low-risk AI applications to comprehensive controls for high-risk AI systems like those used in hiring, creditworthiness assessment, or healthcare diagnostics.
AI System Inventory and Discovery: Implementation begins with comprehensive discovery of all AI technologies in use, including shadow AI deployments where business units have independently adopted AI tools without IT oversight.
Building on the core principles above, scope definition determines how governance resources get allocated and which implementation priorities take precedence, ensuring organizations focus their limited governance resources on AI systems that pose the greatest organizational and regulatory risks.
Transition: With foundational understanding established, the next critical step involves developing practical governance frameworks that translate these concepts into actionable governance structures.

Developing a Governance Framework for AI Governance Implementation
Framework development transforms AI governance concepts into practical structures that organizations can operationalize. Unlike academic frameworks, implementation-focused governance frameworks must integrate seamlessly with existing corporate governance, risk management frameworks, and compliance processes while addressing specific regulatory requirements.
Aligning with Regulatory Compliance and the AI Act
EU AI Act Implementation Requirements: Organizations operating in or serving EU markets must implement governance frameworks capable of classifying AI systems by risk level, conducting mandatory risk assessments for high-risk AI systems, maintaining comprehensive technical documentation, and establishing human oversight mechanisms for AI decisions affecting individuals.
NIST AI Risk Management Framework Integration: US-based organizations often anchor their implementation around NIST’s four core functions: Govern (establishing governance culture and policies), Map (identifying AI related risks and contexts), Measure (analyzing and assessing risks), and Manage (mitigating and monitoring risks throughout the AI lifecycle).
Documentation and Audit Readiness: Both frameworks require implementing governance processes that generate audit-ready documentation, including data lineage records, model validation reports, bias testing results, and incident response logs that demonstrate compliance during regulatory examinations.
Policy Integration Methodology for Responsible AI Governance
Embedding AI Governance into Corporate Governance: Rather than creating standalone AI policies, effective implementation integrates AI-specific requirements into existing governance structures like enterprise risk management, IT governance, and data governance frameworks.
Data Governance and Privacy Policy Coordination: Since AI systems depend heavily on data quality and often process personal information, AI governance implementation must align closely with existing data governance policies and data protection frameworks to ensure consistent oversight of data privacy and data integrity.
Unlike standalone AI policies that often get ignored or bypassed, integrated approaches ensure that AI governance becomes a natural extension of familiar organizational processes, increasing adoption rates and compliance consistency.
Stakeholder Engagement Framework and Organizational Values
Cross-Functional Governance Committee Formation: Implementation requires establishing AI governance committees that include representatives from legal, compliance, information security, risk management, data engineering, HR, and key business units that deploy AI systems.
Executive Sponsorship and Board Reporting: Successful implementation depends on visible executive commitment, typically through C-level sponsorship and regular board reporting on AI governance metrics, AI related risks, risk incidents, and compliance status.
Change Management and Communication Strategies: Since AI governance affects multiple organizational functions, implementation must include comprehensive communication plans that explain governance benefits, address concerns about innovation constraints, and provide clear guidance on new processes aligned with organizational values.
Transition: With governance frameworks designed and stakeholder alignment secured, organizations can proceed to systematic implementation through structured phases.


Step-by-Step AI Governance Implementation Process
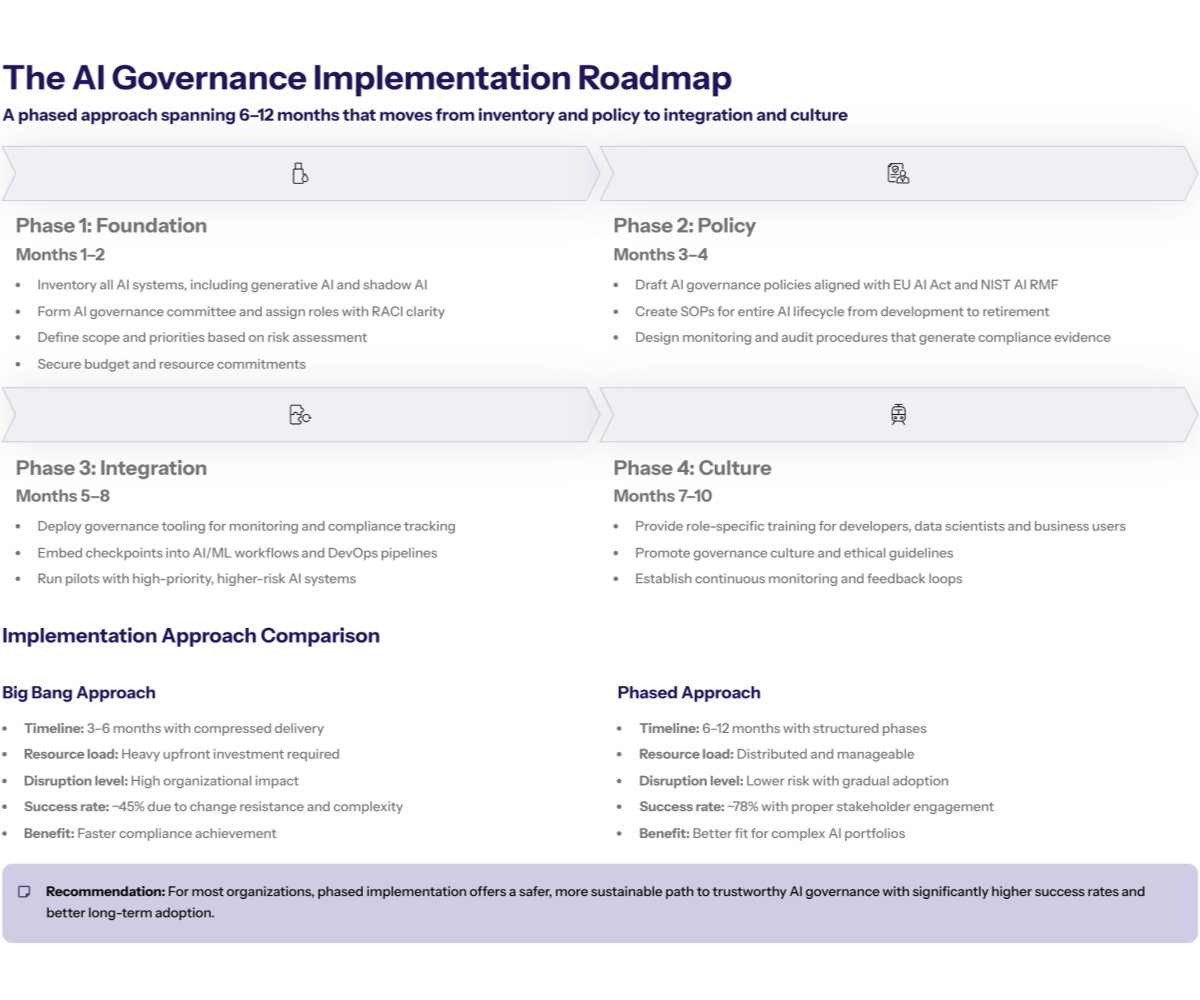
Practical AI governance implementation typically spans 6-12 months depending on organizational size and AI system complexity. The phased approach outlined below has proven effective across organizations ranging from mid-size companies to large enterprises implementing comprehensive AI governance programs.
Step-by-Step: Complete AI Governance Implementation
When to use this: Organizations implementing AI governance for the first time or significantly upgrading existing governance to meet regulatory requirements like the EU AI Act.
-
Phase 1: Foundation and Planning (Months 1-2): Conduct comprehensive AI system inventory to identify all AI technologies currently in use, including generative AI tools and shadow AI deployments. Establish AI governance committee with executive sponsor and assign specific roles using RACI matrix methodology. Define implementation scope based on risk assessment and secure necessary budget and resources.
-
Phase 2: Policy Development and Documentation (Months 3-4): Create AI governance policies aligned with applicable regulatory frameworks (EU AI Act, NIST AI Risk Management Framework). Develop standard operating procedures for each phase of the AI lifecycle from model development through retirement. Design monitoring protocols and audit procedures that generate compliance-ready documentation.
-
Phase 3: Technology and Process Integration (Months 5-8): Implement governance tools for AI system monitoring and compliance tracking. Integrate governance checkpoints into existing AI development workflows and DevOps processes. Deploy automated compliance monitoring for key governance requirements and conduct pilot testing with selected high-priority AI systems.
-
Phase 4: Training and Change Management (Months 7-10): Deliver role-specific training programs for AI developers, data scientists, and business users. Implement governance culture initiatives that reinforce ethical guidelines and responsible AI governance practices. Establish continuous monitoring processes and feedback mechanisms for ongoing governance effectiveness.
Comparing Implementation Approaches for Trustworthy AI
Feature |
Big Bang Implementation |
Phased Implementation |
|---|---|---|
Timeline |
3-6 months |
6-12 months |
Risk Level |
High disruption potential |
Lower change management risk |
Resource Requirements |
Intensive upfront investment |
Distributed resource allocation |
Regulatory Compliance |
Faster compliance achievement |
Gradual compliance building |
Organization Size Fit |
Small to medium organizations |
Large enterprises with complex AI portfolios |
Success Rate |
45% due to change resistance |
78% with proper stakeholder engagement |
The phased implementation approach is recommended for most organizations because it allows for iterative learning, stakeholder adaptation, and course corrections based on early results, leading to more sustainable governance adoption.
Transition: Even with systematic implementation planning, organizations encounter predictable challenges that require proactive solutions.

Common Challenges in Implementing AI Governance and Solutions
Organizations implementing AI governance face recurring obstacles that can derail even well-planned initiatives. The following evidence-based solutions address the most frequent implementation roadblocks encountered across industries and organization types.
Challenge 1: Lack of Executive Buy-In and Resource Allocation
Solution: Develop a comprehensive business case that quantifies both AI governance benefits and non-compliance risks. Present concrete regulatory penalty scenarios—AI Act violations can result in fines up to 7% of global annual revenue, while governance-related incidents have cost individual organizations between $5-50 million in remediation, legal costs, and lost revenue.
Demonstrate ROI through improved AI system performance, reduced compliance costs, faster regulatory approvals, and enhanced stakeholder trust that supports business growth and competitive positioning.
Challenge 2: Cross-Functional Coordination Difficulties
Solution: Establish clear RACI matrices that specify who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed for each governance activity across the AI lifecycle. Implement structured governance committee meetings with standardized agendas, decision-making processes, and action item tracking.
Deploy collaborative platforms that provide shared visibility into AI governance policies, compliance status, and implementation progress across all organizational functions involved in AI initiatives.
Challenge 3: Technical Integration with Existing Systems
Solution: Conduct thorough technical assessments before selecting governance tools, prioritizing solutions with robust API integration capabilities and compatibility with existing MLOps platforms and data infrastructure.
Plan systematically for data migration requirements, ensuring that governance implementations can leverage existing data governance investments rather than creating parallel systems that increase complexity and maintenance overhead.
Challenge 4: Keeping Pace with Rapidly Evolving AI Regulations
Solution: Design governance frameworks with built-in flexibility that can adapt to regulatory changes without requiring complete restructuring. Subscribe to specialized regulatory monitoring services and industry guidance from organizations like OECD AI principles working groups.
Establish quarterly policy review cycles that assess regulatory developments and update governance practices accordingly, ensuring that AI governance frameworks remain current with evolving legal and ethical requirements.
Transition: With solutions to major implementation challenges in place, organizations can focus on next steps for operationalizing their AI governance programs.


Conclusion and Next Steps for Responsible AI Governance
Successful AI governance implementation requires a structured approach that balances regulatory compliance requirements with operational efficiency and innovation objectives. Organizations that invest in systematic implementation—including proper stakeholder engagement, phased deployment, and continuous monitoring—achieve significantly higher success rates in deploying AI systems responsibly while meeting business objectives and regulatory obligations.
The most effective implementations treat AI governance not as a constraint on AI development, but as an enabler of trustworthy AI systems that deliver sustainable business value while protecting organizational reputation and stakeholder trust.
To get started:
-
Conduct a comprehensive AI system audit to identify current governance gaps and regulatory exposure across all AI technologies in use
-
Form a cross-functional AI governance committee with clear executive sponsorship and defined decision-making authority
-
Begin pilot implementation with your highest-risk AI systems to build governance capabilities while addressing priority compliance requirements
Related Topics: Explore AI risk management frameworks for optimizing ongoing governance operations, investigate automated compliance monitoring tools for scaling governance across large AI portfolios, and consider AI ethics training programs for building organizational governance culture that supports responsible AI usage.


Additional Resources
-
EU AI Act Compliance Checklist: Timeline templates and requirement mapping tools for organizations implementing AI governance to meet EU regulatory obligations
-
AI Governance RACI Templates: Pre-configured responsibility matrices for common AI governance roles and activities across the AI lifecycle
-
Implementation Roadmap Templates: Customizable project plans with milestones, resource requirements, and success metrics for AI governance implementation initiatives

