AI Implementation Challenges in Business: Complete Guide to Overcoming Common Obstacles
AI implementation challenges in business have become the defining obstacle for digital transformation in 2025, with 88% of organizations now using AI but most remaining trapped in pilot phases according to 2024 McKinsey research.** While artificial intelligence adoption has reached unprecedented levels across industries, the gap between AI adoption intentions and successful enterprise-wide implementation continues to widen, leaving many organizations struggling to achieve meaningful business value from their AI investments.
This guide addresses the critical disconnect between AI pilot success and production deployment that affects the vast majority of enterprises attempting to scale AI technologies and gen AI initiatives.
What This Guide Covers
This comprehensive resource examines seven major categories of AI implementation challenges, from technical infrastructure obstacles to organizational culture resistance. You’ll discover specific solutions and mitigation strategies for each challenge type, backed by real-world data and proven frameworks. This guide does NOT cover basic AI concepts, vendor selection criteria, or industry-specific use cases—instead, it focuses exclusively on overcoming adoption challenges that prevent AI initiatives from achieving enterprise-wide success.
Who This Is For
This guide is designed for CTOs, IT directors, digital transformation leaders, and business leaders leading AI initiatives within their organizations. Whether you’re an organization stuck in AI pilot purgatory seeking to scale enterprise-wide, or a company beginning AI implementation wanting to avoid common pitfalls that derail 67% of AI projects, you’ll find actionable strategies to navigate implementation complexity.
Why This Matters
Recent studies reveal that 51% of AI-using organizations have experienced negative AI consequences, including ethical concerns and intellectual property infringement, while only 33% of companies successfully scale AI beyond pilots to achieve enterprise-wide impact. The stakes are significant: AI high-performers report 5%+ EBIT impact, while failed implementations result in substantial financial losses and competitive disadvantage. Understanding and proactively addressing these key challenges determines whether your AI journey delivers transformational business value or joins the majority of stalled initiatives.
What You’ll Learn:
-
The seven most critical AI implementation challenges facing businesses today and their interconnected effects
-
Proven strategies to overcome data quality issues, skills gaps, and legacy system integration obstacles
-
How to build organizational readiness and manage cultural resistance to AI adoption
-
Risk mitigation approaches to mitigate AI risks related to data privacy, security concerns, and model outputs that protect business operations


Understanding AI Implementation Complexity and AI Adoption Challenges
AI implementation represents the process of integrating artificial intelligence capabilities into existing business operations and workflows, fundamentally transforming how organizations process information, make decisions, and deliver value to customers.
Unlike traditional software deployment, implementing AI requires organizations to navigate probabilistic systems that learn and adapt rather than following predetermined logic paths. This fundamental difference means AI systems introduce uncertainty, require continuous monitoring, and demand new approaches to quality assurance, performance management, and risk mitigation. AI implementation challenges emerge from this complexity, as organizations must simultaneously manage technical infrastructure, data architecture, and organizational change to achieve successful integration.
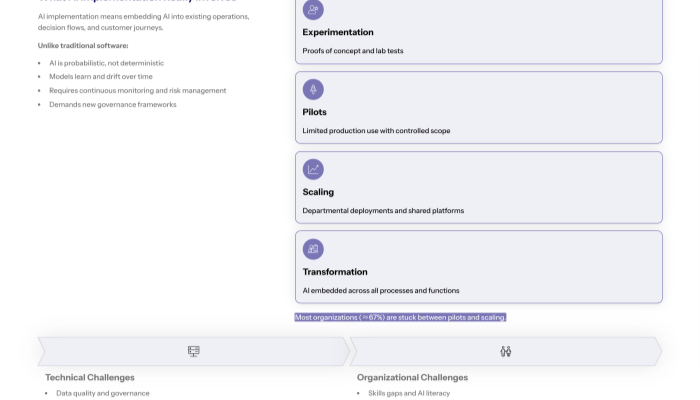
The Implementation Maturity Spectrum and AI Adoption
The AI implementation maturity spectrum encompasses four distinct stages: experimentation (proof-of-concept development), pilot programs (limited production testing), scaling (departmental deployment), and enterprise transformation (organization-wide integration). Understanding this progression is crucial because different adoption challenges dominate each stage, and solutions that work for pilots often fail during scaling phases.
This connects to AI implementation complexity because most organizations—67% according to recent research—remain stuck between pilot and scaling phases, unable to translate promising proof-of-concept results into sustainable business processes that deliver consistent value from AI models and gen AI capabilities.
Technical vs Organizational Challenges in AI Use
Building on the implementation maturity concept, AI adoption challenges fall into two primary categories: technical challenges involving data quality, infrastructure capacity, AI integration, and system integration; and organizational challenges encompassing skills gaps, cultural resistance, and change management requirements.
While technical issues often receive primary attention from technology leaders and data engineers, research indicates that organizational readiness problems frequently masquerade as technical obstacles, creating a misleading focus on infrastructure solutions when cultural transformation is actually required.
Transition: Understanding this dual nature of AI implementation challenges provides the foundation for examining specific technical obstacles that organizations encounter when integrating AI solutions with existing infrastructure.

Data and Infrastructure Challenges in AI Solutions
Data and infrastructure challenges represent the most frequently cited obstacles to successful AI implementation, with nearly half of business leaders identifying these technical barriers as primary impediments to scaling AI initiatives across their organizations.
Data Quality, Training Data, and Availability Issues
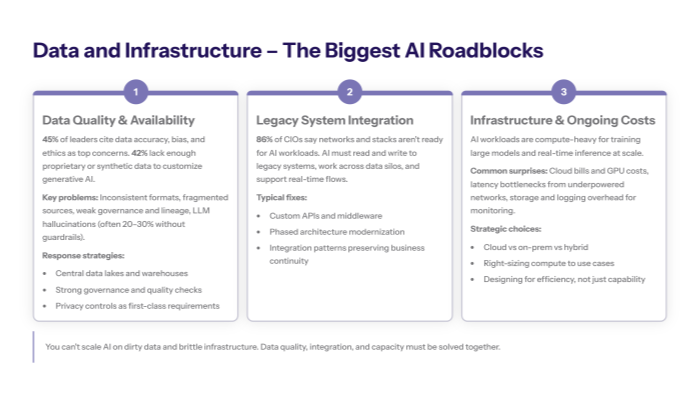
Data quality emerges as the fundamental challenge affecting AI implementation success, with 45% of business leaders citing data accuracy, bias, and ethical concerns as their top concern when deploying AI systems. An additional 42% report lacking sufficient proprietary or synthetic data to customize gen AI models effectively for their specific business requirements, creating a double challenge of quality and quantity.
Legacy deterministic systems struggle to handle the unstructured, multimodal AI workloads that modern AI applications require, while poor data quality directly impacts model outputs and contributes to hallucination rates of 20-30% in large language models. This challenge compounds as organizations attempt to scale beyond pilots, where small datasets may have masked underlying data quality issues that become critical at enterprise scale.
Organizations must invest in robust data infrastructure, often involving cloud migration and centralized data lakes that consolidate information from disparate sources while establishing comprehensive data governance frameworks that ensure consistency, accuracy, and compliance with data privacy and protection regulations across all AI initiatives.
Legacy System Integration Complexity and AI Integration
Unlike data quality issues that can be addressed through governance and infrastructure investment, integration problems require fundamental architectural changes to existing technology stacks. Research indicates that 86% of CIOs believe their enterprise networks are unprepared for AI demands, particularly the real-time processing and computational requirements that AI systems and AI agents introduce.
Integration challenges manifest when AI systems must connect with existing infrastructure and navigate data silos that prevent unified access to organizational information. Many enterprises run on decades-old infrastructure never designed to work with modern AI workflows, creating friction that increases implementation costs and complexity exponentially.
Solutions include developing custom APIs and middleware systems that enable seamless connectivity between AI applications and legacy systems, while gradually modernizing infrastructure through phased migration strategies that maintain business continuity during transformation.
Infrastructure, Ongoing Costs, and Performance Requirements
AI workloads impose significant computational demands for both training and inference processes, requiring organizations to reassess their infrastructure capacity and performance capabilities. High computational costs, particularly for training large gen AI models and supporting real-time AI applications, often exceed initial budget projections and create ongoing operational expenses that many organizations underestimate.
Network capacity limitations can severely impact real-time AI applications, especially those requiring low latency responses or processing large volumes of unstructured data. Organizations must carefully evaluate cloud versus on-premises deployment strategies based on their specific performance requirements, secure data needs, and cost constraints.
Key Points:
-
Data quality affects 45% of implementations and requires governance frameworks before AI deployment
-
Legacy system integration demands architectural changes, not just connectivity solutions
-
Infrastructure costs and ongoing costs often exceed initial projections due to computational and storage demands
Transition: While technical challenges create significant barriers, organizational and cultural factors often determine whether technically sound AI systems achieve adoption and deliver sustained business value.

Organizational and Cultural Barriers to Adopt AI
Building on the technical complexity of AI implementation, human factors represent equally critical obstacles that can derail even well-designed AI systems when organizations fail to address skills gaps, cultural resistance, and change management requirements that successful AI adoption demands.
Skills and In-House Expertise Gaps
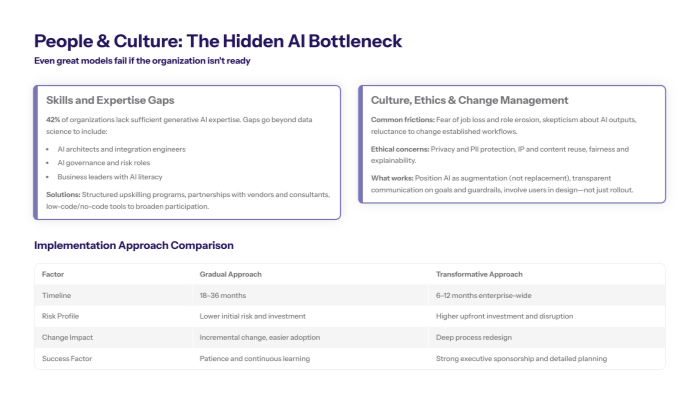
The skills shortage affecting AI implementation manifests across multiple dimensions, with 42% of organizations reporting inadequate generative AI expertise among their workforce. This shortage extends beyond data scientists and machine learning engineers to include AI governance professionals, prompt engineers, and business stakeholders with AI literacy sufficient to guide strategic implementation decisions.
Critical skills gaps emerge in areas including AI model customization, integration architecture, ethical AI governance, and change management for AI transformation. Many organizations discover that technical talent alone is insufficient—they also need individuals who understand how to operationalize AI at enterprise scale while managing organizational change and stakeholder concerns.
When to address this: Skills development becomes critical for moving beyond pilot phases to enterprise scaling, as pilot success often relies on a small team of experts while enterprise implementation requires broader organizational capability.
Solutions include: Comprehensive upskilling programs that develop AI literacy across business functions, strategic partnerships with AI vendors and consulting firms that provide specialized expertise, and adoption of low-code/no-code AI tools and platforms that democratize AI development capabilities while building internal competency.
Cultural Resistance, Ethical Concerns, and Change Management
Employee fears about AI replacing jobs and disrupting established workflows create substantial resistance that undermines adoption of even technically superior AI systems. This resistance manifests in reluctance to share data with AI systems, avoidance of AI-enhanced processes, and skepticism about AI outputs that reduces the practical value AI systems deliver.
Leadership challenges in communicating AI as augmentation rather than replacement require deliberate change management strategies that address employee concerns while building confidence in AI capabilities. Successful cultural transformation involves building AI literacy throughout the organization, establishing continuous learning programs, and redesigning roles to emphasize human-AI collaboration rather than replacement.
Ethical concerns, including data privacy, protection of personally identifiable information, and intellectual property infringement, must be proactively addressed through transparent policies and governance frameworks to build trust and ensure compliance.
Effective change management for AI transformation requires transparent communication about AI goals, comprehensive training that builds confidence and competence, and active involvement of employees in AI implementation decisions rather than imposing changes through top-down mandates.
Comparison: Gradual vs Transformative AI Implementation
Feature |
Gradual Approach |
Transformative Approach |
|---|---|---|
Timeline |
18-36 months across phases |
6-12 months enterprise-wide |
Resource Requirements |
Lower initial investment, sustained commitment |
High upfront investment, concentrated effort |
Risk Level |
Lower risk of major disruption |
Higher risk but faster competitive advantage |
Organizational Impact |
Incremental change, easier adoption |
Fundamental transformation, requires strong leadership |
Success Factors |
Continuous learning, patience |
Executive sponsorship, comprehensive planning |
Organizations with lower AI maturity and risk tolerance typically benefit from gradual approaches that build capability progressively, while companies facing competitive pressure or with strong change management capability may succeed with transformative implementation strategies. |
Transition: Beyond organizational readiness, strategic alignment and financial planning determine whether AI implementation efforts translate into measurable business outcomes that justify continued investment.

Strategic and Financial Implementation Challenges for AI Adoption
Strategic and financial barriers often prove more challenging to overcome than technical obstacles, as they require organizations to align AI capabilities with business objectives while demonstrating clear returns on investment that justify ongoing resource allocation.
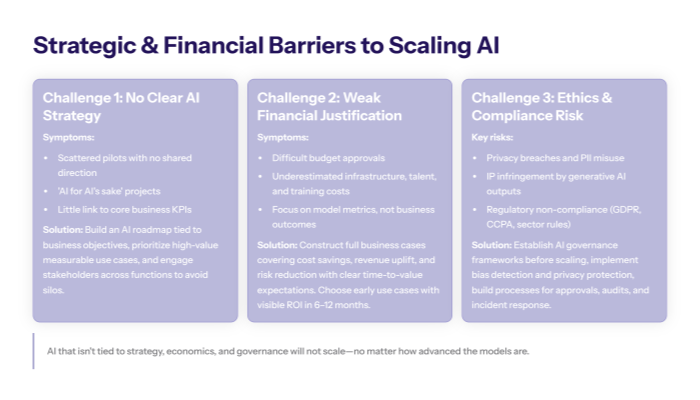
Challenge 1: Lack of Clear AI Strategy and Vision for AI Use
Solution: Develop comprehensive AI roadmaps aligned with business objectives and identify high-value use cases with measurable ROI potential that address specific operational constraints or competitive opportunities.
Cross-departmental stakeholder engagement ensures shared understanding of AI goals while preventing siloed implementations that fail to deliver enterprise-wide value. Successful AI strategies focus on business processes with quantifiable efficiency gains rather than pursuing AI adoption for technological novelty.
Challenge 2: Inadequate Financial Justification and Training Costs
Solution: Build comprehensive business cases that highlight specific cost savings, revenue growth opportunities, and competitive advantages that AI implementation will deliver within defined timeframes.
Focus on automating business processes with clear efficiency gains and quantifiable impact on key performance indicators. Organizations achieve stronger financial justification by targeting repetitive, high-cost processes for AI enhancement while establishing baseline metrics that demonstrate improvement over time.
Training costs for AI specialists and data engineers should be factored into financial planning, along with ongoing costs related to maintaining AI solutions and infrastructure.
Challenge 3: Ethical and Compliance Risk Management Including Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Solution: Establish comprehensive AI governance frameworks, ethical guidelines, and regulatory compliance processes before deploying AI systems in production environments that handle sensitive data or make decisions affecting individuals.
Implement bias detection systems, privacy protection measures, and transparency mechanisms that ensure AI outputs are explainable and compliant with data protection regulations. Proactive risk management helps mitigate AI risks related to intellectual property, data privacy, and security concerns, preventing costly legal issues while building stakeholder confidence in AI initiatives.
Transition: Successfully addressing these strategic challenges requires coordinated action across multiple organizational dimensions to achieve sustainable AI transformation.

Conclusion and Next Steps for Successful AI Integration
Successful AI implementation requires organizations to simultaneously address technical infrastructure challenges, organizational culture barriers, and strategic alignment issues rather than treating these as sequential problems to solve independently. The interconnected nature of AI implementation challenges means that solving data quality issues without addressing skills gaps, or improving technical capabilities without managing cultural change, typically results in stalled initiatives that fail to achieve enterprise-wide transformation.
To get started:
-
Conduct comprehensive AI readiness assessment across technical infrastructure, data quality, and organizational capabilities to identify the most critical gaps preventing successful integration
-
Develop focused pilot program addressing one specific business challenge with clear success metrics, stakeholder involvement, and scalability potential
-
Build cross-functional AI implementation team including technical expertise, business domain knowledge, and change management capabilities essential for navigating implementation complexity
Related Topics: AI governance frameworks provide essential structure for managing risk and compliance, while data management best practices and change management methodologies offer deeper guidance on foundational capabilities that support successful AI transformation initiatives.


Additional Resources
For organizations seeking to accelerate their AI implementation journey, consider establishing partnerships with AI specialists who can provide domain expertise while internal teams develop capabilities, and investing in AI platforms and ai tools that offer pre-built integrations with legacy systems to reduce technical complexity during initial deployment phases.
AI Agents and Their Role in AI Adoption
AI agents, which are autonomous systems capable of acting in the real world by planning and executing multiple steps in workflows, represent a growing frontier in AI use. Organizations scaling AI agents report improvements in efficiency and customer satisfaction by automating complex tasks in IT service management, knowledge management, and other business functions.
Successful integration of AI agents requires addressing unique challenges, including managing model outputs, ensuring secure data handling, and mitigating AI risks related to operational constraints and ethical concerns. Developing in-house expertise and leveraging gen AI capabilities can accelerate adoption and maximize the benefits of AI agents in business operations.

