Understanding Cloud Computing and Edge AI
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, the question "what is cloud computing and edge AI" has become increasingly important. Both concepts represent critical advancements in how we process data and leverage computing power to build smarter, faster, and more efficient systems. Edge computing brings AI capabilities closer to where data is generated, enabling real-time data processing and decision-making on local edge devices without relying heavily on a continuous internet connection.
Meanwhile, cloud computing offers vast computing resources and centralized infrastructure that can analyze data at scale, supporting complex AI workloads and large-scale storage. Understanding the key differences and complementary nature of these technologies is essential for businesses aiming to harness the full potential of artificial intelligence today.
Key Takeaways
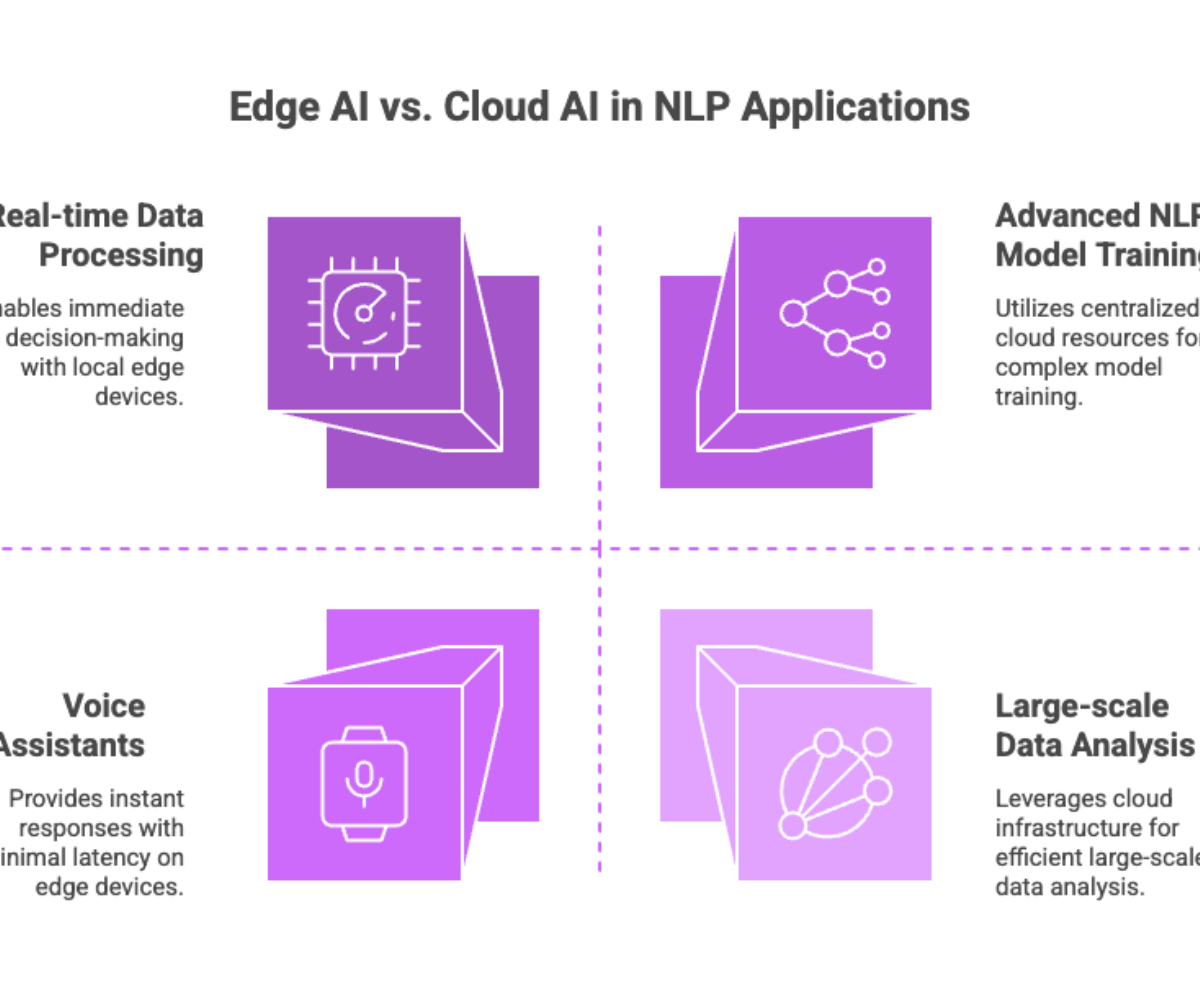
Integration of Edge AI and Cloud AI Enhances NLP Applications: The convergence of edge AI and cloud computing enables efficient natural language processing (NLP) by combining real-time data processing on local edge devices with the vast computational power of cloud platforms for complex language model training and large-scale data analysis.
Edge AI Reduces Latency and Preserves Data Privacy in NLP Tasks: Deploying AI models for NLP directly on edge devices minimizes latency and limits the need for transmitting sensitive data to cloud data centers, enhancing user privacy and enabling immediate real-time decision making in applications like voice assistants and chatbots.
Cloud AI Supports Advanced NLP Model Training and Scalability: While edge AI handles on-device inference, cloud AI leverages cloud infrastructure to train and update sophisticated NLP models using large-scale data processing and machine learning techniques, ensuring continuous improvement and scalability of NLP-powered solutions.

Introduction to Cloud Computing
In today’s digital-first world, cloud computing has become the backbone of modern technology. At its core, cloud computing is the delivery of servers, storage, computing resources, and applications over the internet, giving organizations the ability to scale operations without relying solely on physical infrastructure. Businesses no longer need to invest heavily in on-site data centers; instead, they tap into cloud computing facilities offered by major cloud providers such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
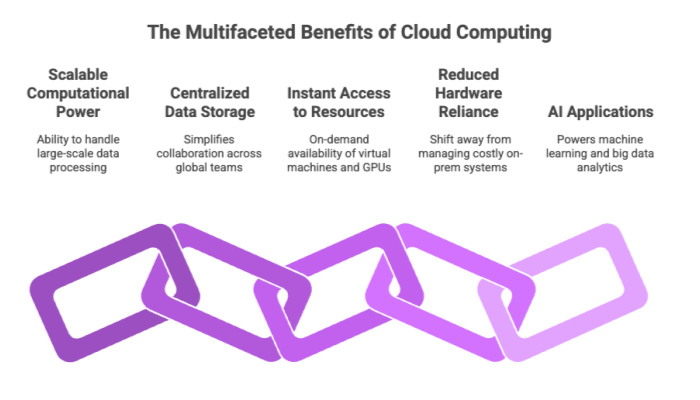
The appeal of cloud computing architecture lies in its ability to offer scalable computational power and centralized data storage. For enterprises running AI applications, this means being able to handle large-scale data processing, train AI models, and store historical data without hitting hardware bottlenecks.
Key benefits of cloud computing for enterprises include:
Instant access to computing resources: Spin up virtual machines, GPUs, or even TPUs on demand.
Centralized data management: Simplifies collaboration across global teams.
Cloud infrastructure scalability: Scale up or down as business needs evolve.
Reduced reliance on local hardware: Shift away from managing costly cloud servers and on-prem systems.
Today, the role of cloud computing extends beyond simple IT support. It is tightly woven into AI applications, powering machine learning, big data analytics, and real-time data processing pipelines. Whether it’s predictive maintenance in manufacturing or object detection in smart cities, cloud computing provides the computational power to make it possible.

Edge AI Overview
While cloud computing offers scale and centralized data centers, it doesn’t always deliver the low latency required for certain tasks. This is where edge AI technology comes in.
Edge AI refers to the deployment of AI models directly on local edge devices such as smartphones, IoT devices, smart cameras, and even vehicles. Instead of transmitting data to distant remote servers for inference, edge AI processes data locally, ensuring real-time decision making and immediate data processing.
Why Edge AI Matters?
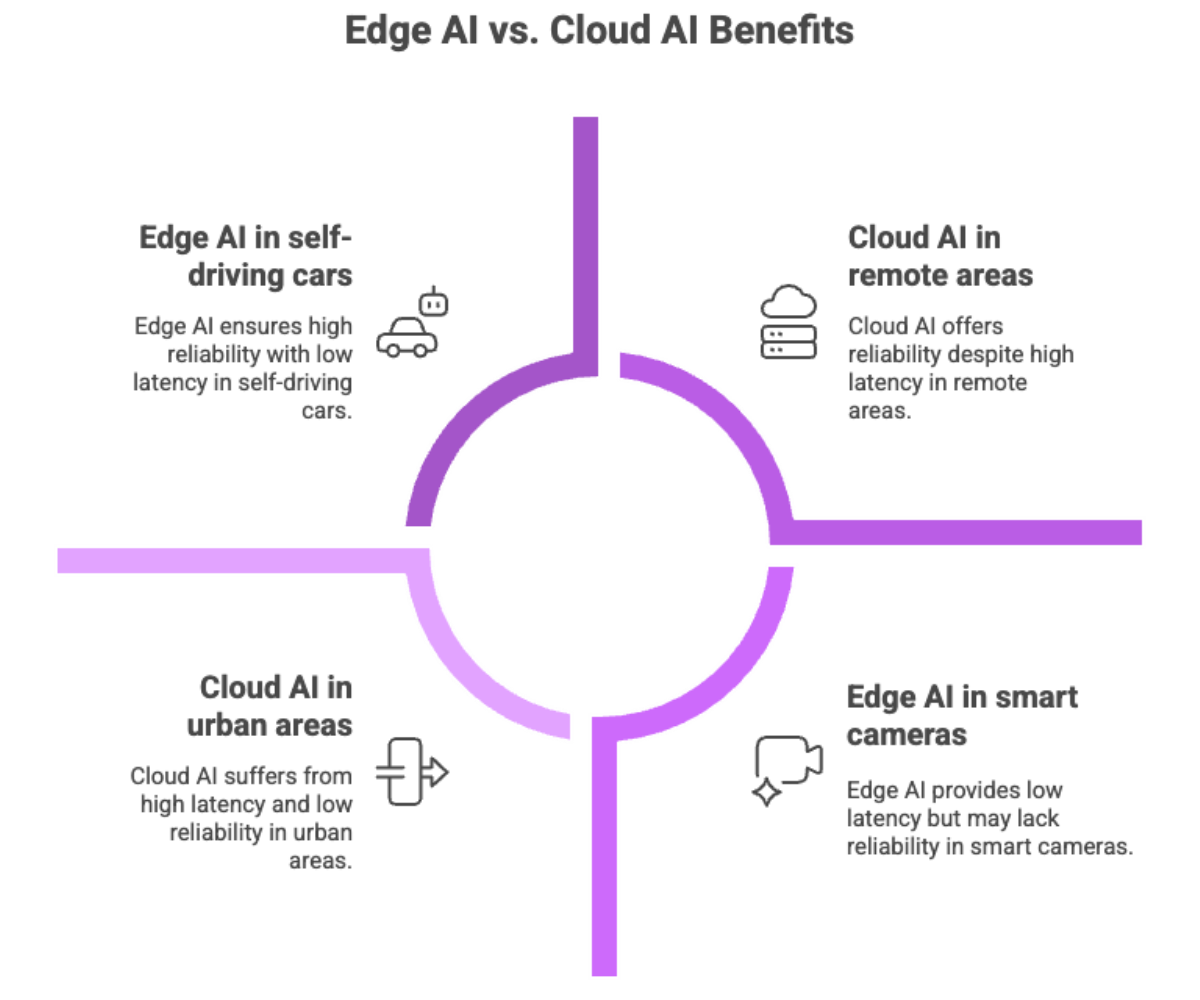
Low Latency: Critical for self-driving cars, robotics, and smart factories, where split-second responses are essential.
High Reliability: Edge AI devices can operate with limited or no internet access, making them useful in environments where connectivity is unreliable.
Data Privacy: Since sensitive data is processed on-device, the risks of data breaches or issues with transmitting sensitive data are minimized.
Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need to send large amounts of sensor data back to the cloud.
Real-World Applications of Edge AI
Smart factories: Robots using edge AI hardware to adjust workflows in real time.
Self-driving cars: Making real-time decision making possible without depending on cloud platforms.
Smart cameras: Performing object detection locally for security or retail analytics.
In essence, edge artificial intelligence empowers organizations to process data locally while maintaining autonomy from cloud reliance. It complements the strengths of cloud AI by handling real-time processing tasks where milliseconds count.

Cloud AI and Artificial Intelligence
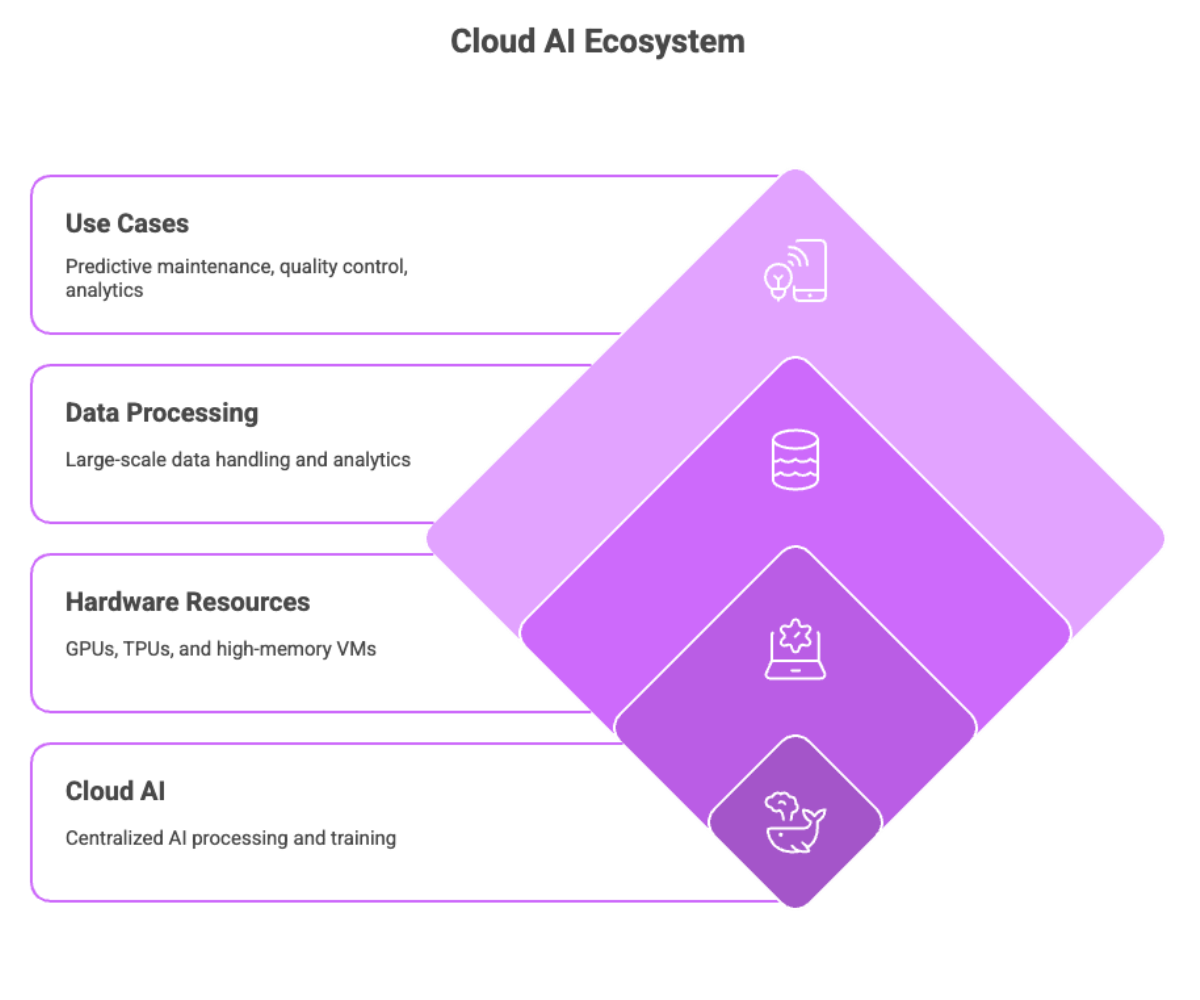
When tasks exceed the limited processing power of edge devices, enterprises turn to cloud AI. Unlike edge AI models optimized for lightweight inference, cloud AI refers to running and training artificial intelligence algorithms in centralized data centers using the full breadth of cloud infrastructure.
How Cloud AI Works?
Cloud AI leverages powerful GPUs, TPUs, and high-memory VMs available on cloud platforms.
It enables large-scale data processing and training of machine learning models.
With virtually unlimited processing power, cloud AI can handle big data analytics and AI algorithms requiring terabytes of data.
Cloud AI Advantages
Scale: Train massive AI models that would overwhelm local infrastructure.
Efficiency: Run batch data processing workloads cost-effectively.
Resource Sharing: Multiple data scientists can collaborate within the same cloud computing environment.
Example Use Cases
Predictive maintenance: Cloud AI analyzes historical data from industrial equipment to predict failures.
Quality control: Factories use cloud infrastructure to analyze thousands of images for defects.
Big data analytics: Healthcare providers analyzing patient records to predict disease outbreaks.
Cloud AI complements edge AI by tackling AI applications that require enormous computational power, vast data storage, and access to specialized hardware.

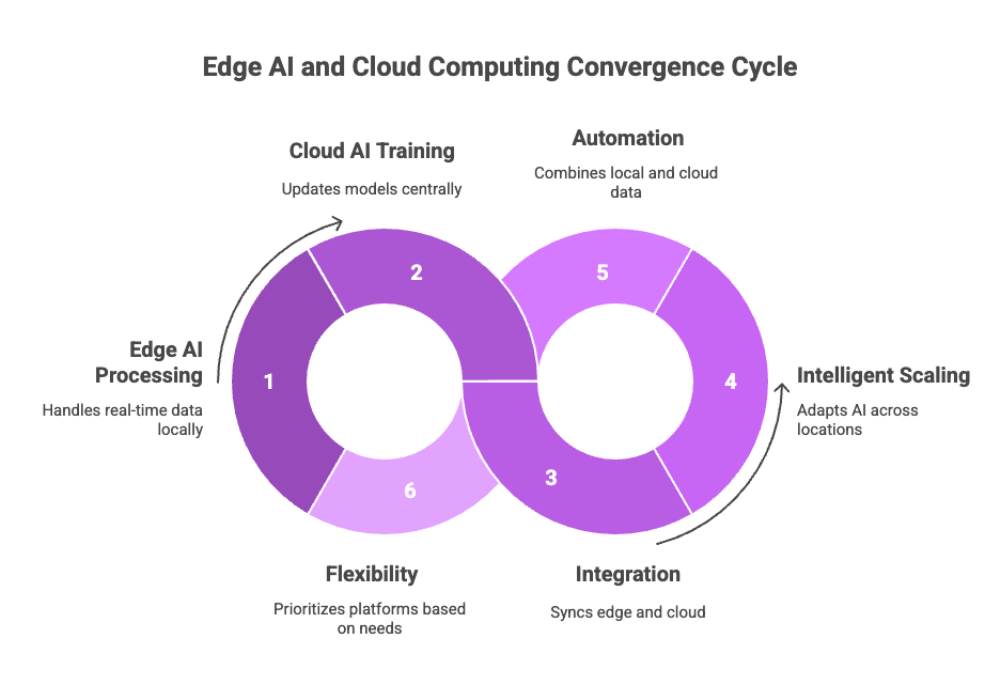
Edge AI and Cloud Computing Convergence
While cloud computing and edge AI have traditionally been seen as separate paradigms, the industry is now witnessing their convergence. The result is an efficient AI ecosystem that leverages the strengths of both.
How the Convergence Works?
Edge AI processes data locally, handling real-time decision making and immediate data processing on edge devices.
Cloud AI focuses on model training, large-scale data analysis, and updating AI models centrally in cloud data centers.
Integration enables intelligent scaling: edge devices execute trained AI models, while cloud computing handles retraining and long-term data management.
Requirements for Success
Stable internet connectivity: To sync edge AI devices with the cloud.
Secure data transmission: Protecting sensitive data when syncing.
Efficient data management: Balancing what is processed locally versus in the cloud.
Advantages of Integrating Edge AI
Intelligent scaling of AI applications across locations.
Automation: Combining local data processing with cloud-based analytics for smarter systems.
Flexibility: Enterprises can prioritize platforms based on latency, cost, or compliance needs.
This edge AI cloud computing convergence forms the backbone of future AI solutions, enabling both real-time processing at the edge and powerful analytics in the cloud.

Data Processing and Analysis
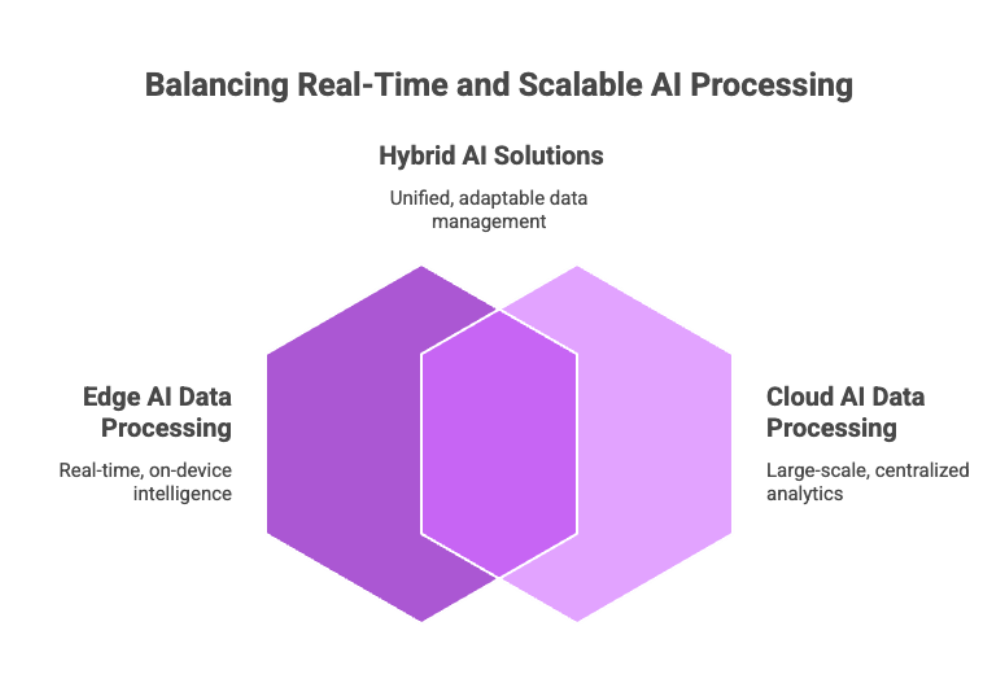
The lifeblood of both cloud AI and edge AI lies in how effectively they manage data processing.
Edge AI Data Processing
Edge AI shines when processing data directly on-device. Instead of sending sensor streams to a cloud, edge AI devices run AI models locally to deliver real-time data processing.
Benefits: Lower latency, reduced bandwidth usage, and higher privacy.
Examples: Smart cameras running edge AI models to detect objects or IoT devices monitoring energy consumption in factories.
Cloud AI Data Processing
On the other hand, cloud AI handles large-scale data processing and big data analytics. This includes:
Batch data processing: Running large jobs overnight.
Analyzing historical data: Critical for predictive analytics.
Training AI models: Leveraging the computational power of cloud data centers.
Key Challenges
Data transmission: Moving massive amounts of sensor data securely.
Stable internet connectivity: Essential for hybrid systems.
Data breaches: A risk if sensitive data isn’t protected during transit.
By combining edge AI for real-time processing and cloud AI for deeper analytics, businesses can balance speed with scale. This dual approach underpins industries like healthcare, finance, and transportation, where both immediate data processing and long-term insights are essential.

AI Applications and Use Cases
The convergence of cloud computing and edge AI has opened the door to a diverse range of AI applications. Each approach has strengths that make it suitable for specific tasks, and in practice, organizations use them together for maximum efficiency.
Edge AI Use Cases
Edge AI technology is best suited for real-time decision making and processing data locally on edge devices.
Smart factories: Robots use edge AI platforms to monitor assembly lines and adapt to changes instantly.
Self-driving cars: Equipped with edge AI hardware, they must process sensor data in milliseconds to ensure safety.
Smart cameras: Handle object detection locally, avoiding delays that would occur if images had to be sent to remote servers.
Here, edge AI shines by combining low latency, reliability, and privacy. These are environments where any delay in real-time processing could compromise performance or safety.
Cloud AI Use Cases
Cloud AI leverages the processing power of centralized data centers for large-scale data processing and AI model training.
Predictive maintenance: Using historical data from machines, cloud AI predicts when failures might occur.
Quality control: Analyzing thousands of images across factories in parallel.
Big data analytics: Running AI algorithms on terabytes of data for financial forecasting or medical research.
These AI applications require cloud infrastructure, massive storage, and advanced cloud services that allow enterprises to run workloads impossible on edge devices.
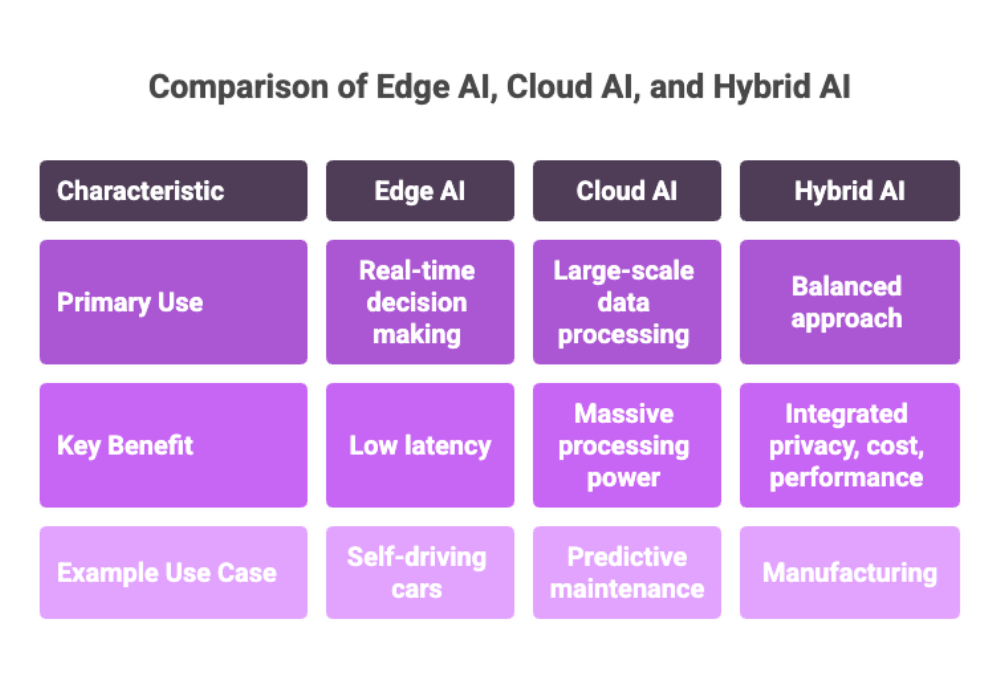
Hybrid AI Use Cases
Increasingly, enterprises use both approaches in tandem:
Manufacturing: Edge AI handles immediate data processing on-site, while cloud systems run big data analytics to optimize supply chains.
Healthcare: Edge artificial intelligence ensures patient monitoring is done locally to protect sensitive data, while the cloud is used for population-level analysis.
Finance: Edge AI devices enable fraud detection in real time, while cloud AI provides deep analysis of historical data.
This combination allows businesses to integrate edge AI with cloud computing in ways that balance privacy, cost, and performance.

Data Management and Security
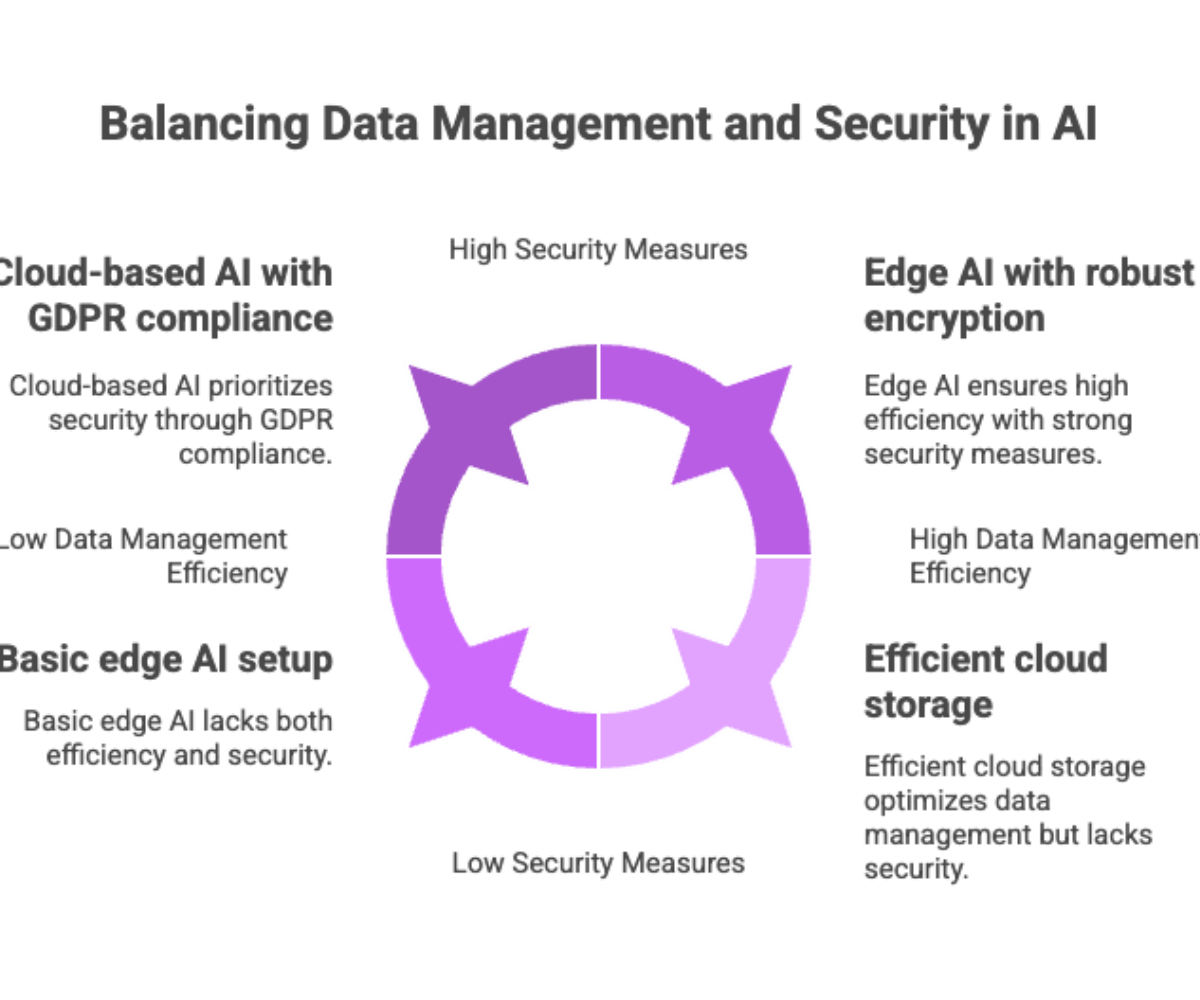
At the heart of both edge AI and cloud computing lies the challenge of data management and security. Without robust frameworks, AI applications risk being derailed by inefficiencies or breaches.
Key Considerations for Data Management
Efficient data processing: Determining what to process data locally and what to send to the cloud.
Stable internet connectivity: Essential for syncing models between edge devices and cloud platforms.
Cloud storage vs. local storage: Balancing centralized repositories with distributed edge AI devices.
Security in Edge AI and Cloud AI
Data breaches: Preventing leaks when transmitting data across networks.
Transmitting sensitive data: Requires encryption and compliance with regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
Local processing advantages: Edge AI devices reduce the need for moving sensitive data into the cloud, thereby minimizing exposure.
Provider Options
Cloud providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer built-in data management tools, while edge AI devices are now shipping with enterprise-grade features like hardware encryption. This means businesses can choose deployment strategies that match their AI solutions and compliance requirements.
In short, successful data management in AI requires a careful balance between the centralized power of cloud computing and the autonomy of edge AI devices.

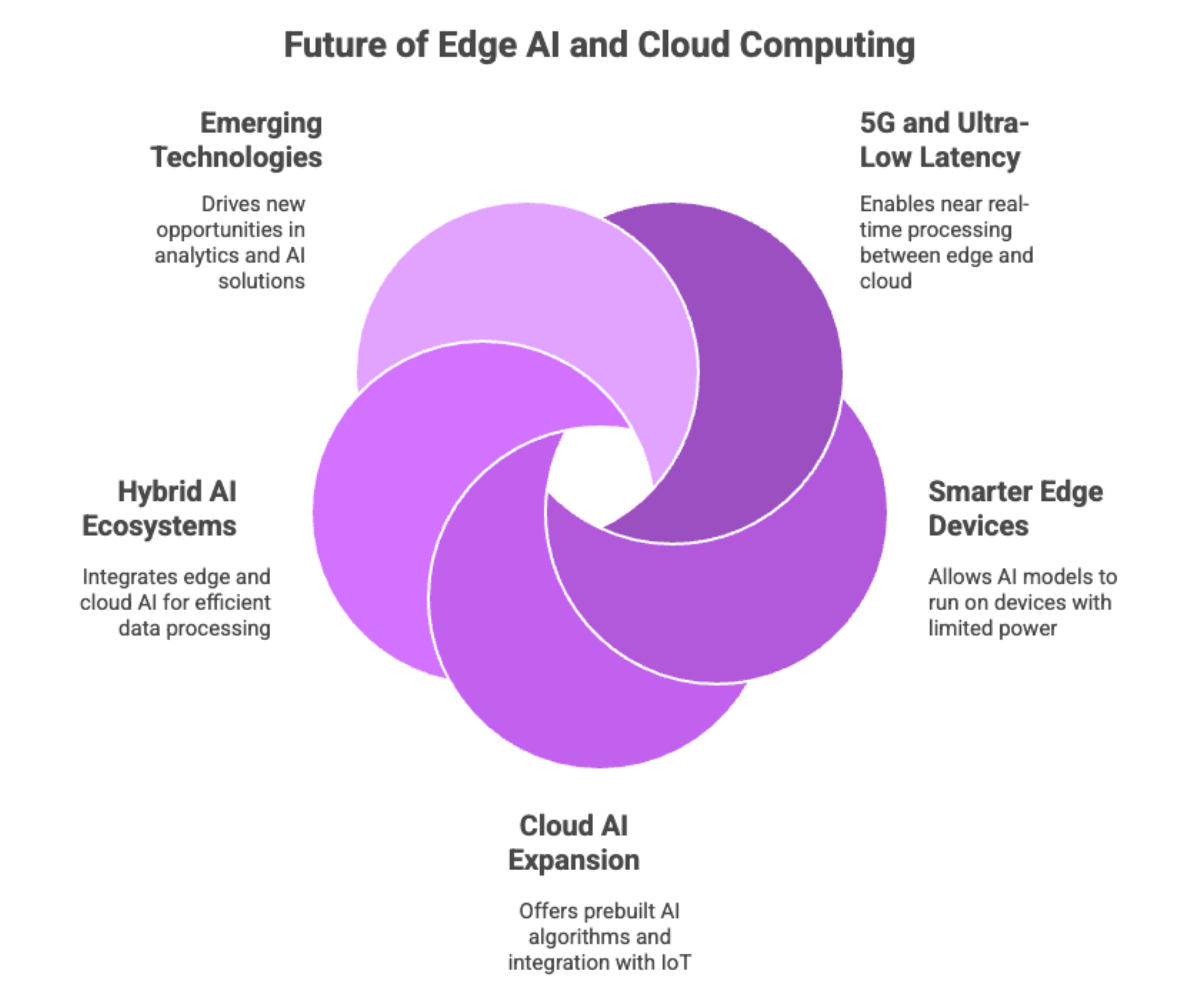
Future Trends and Opportunities
Looking ahead, the future of edge AI and cloud computing is bright. Emerging technologies and evolving cloud infrastructure will continue to reshape how AI applications are deployed and managed.
1. 5G and Ultra-Low Latency
The arrival of 5G networks will reduce reliance on stable internet connectivity by enabling near real-time processing between local edge devices and cloud data centers.
2. Smarter Edge Devices
Edge AI hardware will continue to improve, allowing edge AI models to run on devices with limited processing power while still delivering real-time decision making.
3. Cloud AI Expansion
Cloud platforms will expand their offerings with prebuilt AI algorithms, improved cloud computing architecture, and integration with IoT devices. Expect more pre-trained models and services tailored to industries like healthcare, finance, and logistics.
4. Hybrid AI Ecosystems
The future is not edge versus cloud but integrating edge AI with cloud computing. This convergence will create an efficient AI ecosystem where edge AI processes data instantly, while cloud AI handles large-scale data processing and model retraining.
5. Emerging Technologies
Advances in artificial intelligence, IoT devices, and machine learning will drive new opportunities in predictive analytics, quality control, and big data analytics. Enterprises will increasingly rely on AI solutions that combine local and centralized intelligence.
Businesses that invest now in emerging technologies will be well-positioned to adapt to these opportunities.

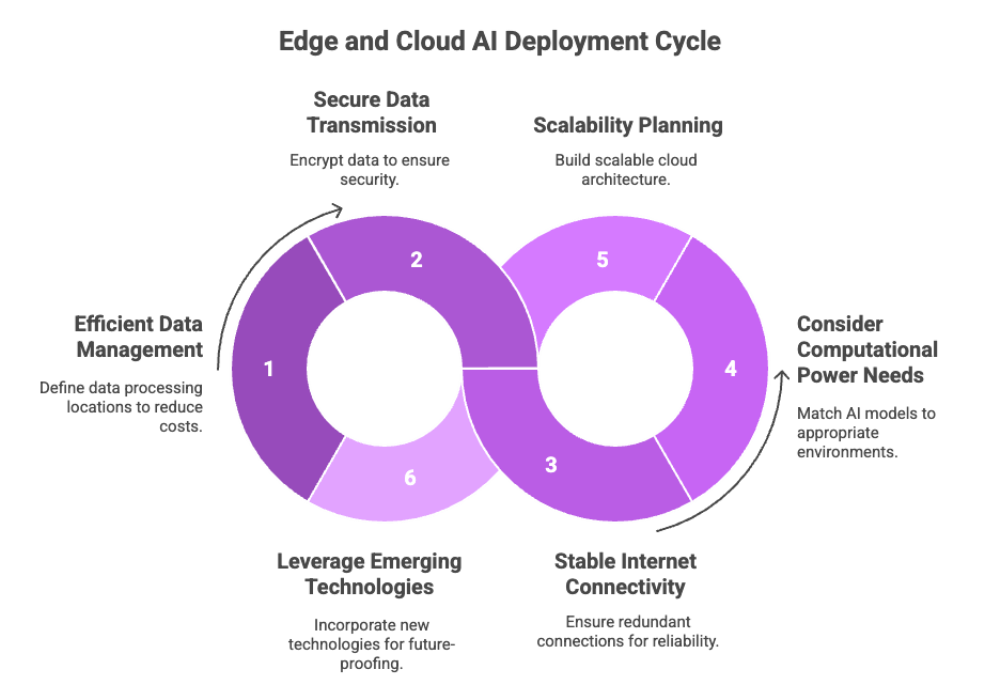
Best Practices for Deployment
Deploying edge AI and cloud computing systems isn’t just about buying hardware or renting servers — it requires thoughtful planning. Following best practices ensures systems deliver optimal performance while minimizing risks.
Deployment Best Practices
Efficient Data Management
Define which data should be processed locally versus in the cloud. This prevents unnecessary transmitting data and reduces costs.
Secure Data Transmission
Encrypt sensitive data at every stage, whether moving between edge devices or stored in cloud storage.
Stable Internet Connectivity
Ensure redundant connections for hybrid deployments to minimize downtime.
Consider Computational Power Needs
Match AI models to the right environment. Use edge AI technology for real-time processing and cloud AI for heavy model training.
Scalability Planning
Build with cloud computing architecture that can scale up computing resources as AI applications grow.
Leverage Emerging Technologies
Incorporate 5G, IoT, and artificial intelligence advances to future-proof your deployment.
By following these best practices, enterprises can deploy edge AI and cloud AI systems that are resilient, cost-efficient, and future-ready.

Conclusion
The synergy between cloud computing and edge AI is creating a new era of artificial intelligence deployment. On one hand, cloud AI refers to massive cloud data centers running machine learning workloads with unmatched computational power. On the other, edge AI processes data locally, offering real-time decision making on edge devices with low latency and enhanced privacy.
Together, they form the foundation of modern AI applications. From predictive maintenance in factories to self-driving cars, from big data analytics in healthcare to object detection in retail, the combined strength of edge and cloud delivers both agility and scale.
As emerging technologies like 5G and IoT mature, the integration of edge AI and cloud computing will only deepen. Businesses that adopt best practices for deployment and embrace this convergence will unlock smarter, faster, and more secure AI solutions, staying competitive in a data-driven future.


