Best Approaches for AI Governance Implementation: Guide for Enterprise Leaders
Best approaches for AI governance implementation require structured methodologies that transform strategic AI governance frameworks into operational reality through cross-functional teams, policy automation, and risk-based monitoring systems. Organizations worldwide recognize that responsible AI governance is no longer optional—it’s a critical business imperative that demands systematic implementation to ensure regulatory compliance, mitigate AI risks, and enable trustworthy AI deployment at scale.
While 79% of enterprise leaders view AI adoption as critical to their business strategy, 60% lack clear implementation vision for AI governance programs, creating dangerous gaps between strategic intent and operational execution.
What This Guide Covers
This guide provides proven implementation methodologies spanning cross-functional team formation to automated monitoring systems, strategic approaches including policy-as-code frameworks and risk-based governance, and phased rollout strategies that accelerate compliance. We exclude theoretical AI governance concepts and focus exclusively on actionable implementation strategies that drive results.
Who This Is For
This guide is designed for CDOs, Chief Risk Officers, compliance teams, and AI program leaders responsible for operationalizing AI governance within their organizations. Whether you’re implementing governance frameworks from scratch or enhancing existing AI governance initiatives, you’ll find specific methodologies to accelerate responsible AI practices while ensuring regulatory compliance and stakeholder trust.
Why This Matters
Poor AI governance implementation leads to regulatory penalties under evolving regulations like the EU AI Act, reputational damage from AI-related incidents, and operational failures that undermine business objectives. Structured implementation approaches prevent governance gaps while enabling responsible AI scale, transforming compliance from a barrier into a competitive advantage that demonstrates trustworthy AI capabilities to customers and regulators.
What You’ll Learn:
-
Cross-functional implementation strategies using governance committees and RACI matrices for clear accountability
-
Policy-driven approaches including automation frameworks and compliance mapping for consistent enforcement
-
Risk-based implementation methodologies enabling continuous monitoring of AI systems and proactive risk management
-
Technology integration approaches for governance platforms and tools that support AI lifecycle management


Understanding AI Governance Implementation Fundamentals
AI governance implementation refers to the systematic operationalization of policies, processes, and technical controls that ensure AI systems operate ethically, safely, and in compliance with regulatory requirements throughout the AI lifecycle.
Unlike theoretical AI governance frameworks that outline principles and objectives, implementation focuses on translating governance strategies into executable workflows, automated controls, and measurable outcomes. Effective AI governance encompasses organizational structures, policy frameworks, monitoring systems, and change management processes that collectively enable responsible AI development and deployment.
AI governance refers to the comprehensive set of practices, standards, and tools designed to enable AI governance practices that promote responsible AI use, mitigate AI related risks, and ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards. This includes managing the entire AI operations lifecycle, from AI development and deployment to monitoring AI systems and evaluating AI outputs for fairness, accuracy, and transparency.
Implementation matters because it bridges the critical gap between strategic AI governance intentions and operational execution. Organizations can develop comprehensive AI governance policies, but without proper implementation, these frameworks remain ineffective documents rather than operational safeguards that protect against AI risks and ensure trustworthy AI outcomes.
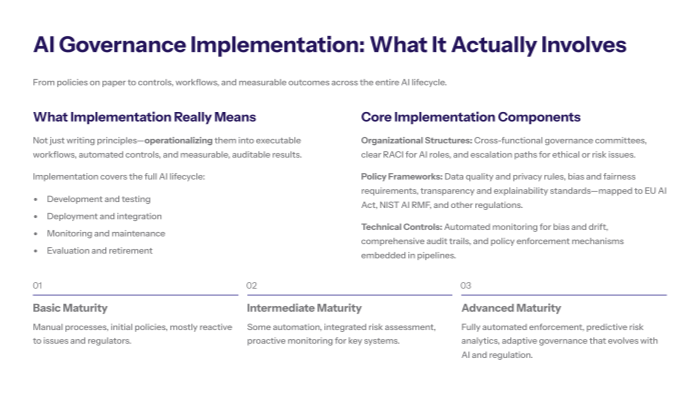
Core Implementation Components
AI governance implementation consists of three interconnected components that work together to operationalize responsible AI practices. Organizational structures include cross-functional governance committees, defined roles and responsibilities through RACI matrices, and escalation paths for AI-related ethical concerns. Policy frameworks encompass comprehensive AI policies addressing data quality management, bias mitigation, transparency requirements, and regulatory compliance mapped to standards like the EU AI Act and NIST AI Risk Management Framework. Technical controls involve automated monitoring systems for bias detection, performance drift monitoring, audit trail capabilities, and policy enforcement mechanisms that ensure AI systems operate within approved parameters.
Data management and data privacy are critical elements embedded within these components, ensuring that sensitive data used in machine learning models is handled securely and ethically, maintaining data integrity and respecting data protection regulations. AI governance frameworks vary across industries and regions, reflecting differences in regulatory environments and organizational risk appetites, but all share these core components to enable robust AI systems.
This connects to AI governance implementation because governance requires operational execution across people, processes, and technology—each component must function effectively for the overall framework to succeed in enabling responsible AI usage while mitigating compliance risks and unintended consequences.
Implementation Maturity Levels
Organizations typically progress through three distinct maturity levels during AI governance implementation. Basic implementation establishes foundational governance structures with manual processes, initial policy documentation, and reactive risk management approaches focused on immediate compliance requirements. Intermediate implementation introduces automated monitoring capabilities, integrated risk assessment processes, and proactive governance mechanisms that begin to scale with AI adoption. Advanced implementation features fully automated policy enforcement, predictive risk analytics, and adaptive governance frameworks that evolve with changing regulatory requirements and organizational needs.
Building on core components, maturity levels guide phased implementation approaches that allow organizations to develop governance capabilities incrementally while maintaining operational effectiveness and avoiding governance overhead that could slow AI initiatives.
Transition: Understanding these fundamentals provides the foundation for selecting strategic approaches that align with your organization’s current maturity level and business objectives.

Strategic Approaches to AI Governance Implementation
Organizations must choose strategic methodologies that align governance implementation with their risk tolerance, regulatory environment, and AI adoption goals while ensuring scalable and sustainable responsible AI practices.
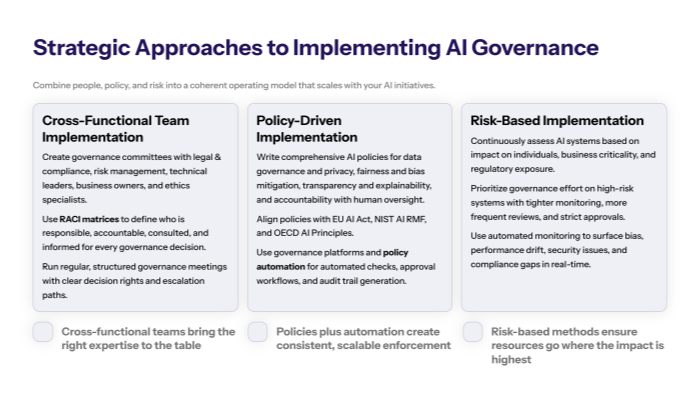
Cross-Functional Team Implementation
Successful AI governance implementation requires establishing diverse governance committees that include legal teams for regulatory compliance, ethics specialists for moral implications and ethical guidelines, risk management professionals for AI risk assessment, technical leads for implementation feasibility, and business unit representatives for operational alignment. These teams use RACI matrices to define clear roles and responsibilities—ensuring no ambiguity about who owns specific AI governance decisions, who contributes expertise, who must be consulted for approvals, and who needs information about governance outcomes. Regular governance committee meetings with structured agendas, decision-making authority, and escalation paths create accountability mechanisms that prevent governance paralysis while maintaining oversight of AI initiatives across the organization.
Cross-functional collaboration addresses the reality that AI governance requires expertise spanning legal, technical, ethical, and business domains—no single function possesses sufficient knowledge to implement comprehensive governance independently. This approach also incorporates ethical considerations and ethical AI practices to guide AI development and deployment, ensuring that generative AI and other advanced AI technologies are developed responsibly.
Policy-Driven Implementation
Policy-driven approaches develop comprehensive AI policies that address data governance requirements, fairness and bias mitigation standards, transparency and explainability mandates, and accountability mechanisms for AI outcomes throughout the AI lifecycle. These policies integrate directly with regulatory frameworks including EU AI Act compliance requirements, NIST AI Risk Management Framework guidance, and OECD AI Principles to ensure alignment with evolving regulations and industry best practices. Policy automation through governance platforms enables consistent enforcement at scale, reducing manual burden while maintaining compliance through automated policy checks, approval workflows, and audit trail generation.
Unlike ad-hoc governance approaches that rely on individual judgment, policy-driven implementation provides consistent governance standards that scale with AI adoption while reducing compliance risks and ensuring predictable outcomes across diverse AI applications and use cases. This approach also addresses data protection and data privacy requirements critical to maintaining trust and legal compliance.
Risk-Based Implementation
Risk-based approaches implement continuous risk assessment processes that evaluate AI systems based on their potential impact on individuals, organizations, and society while prioritizing governance resources on highest-risk AI applications. Automated monitoring systems detect bias in AI models, performance drift that could affect AI outcomes, security vulnerabilities that expose sensitive data, and regulatory compliance gaps that create legal exposure. Proactive risk management processes include incident response protocols, remediation workflows, and continuous improvement mechanisms that adapt governance practices based on emerging AI risks and operational experience.
Risk-based implementation recognizes that governance resources are finite and must be allocated strategically to maximize protection while enabling innovation through differentiated approaches for high-risk versus low-risk AI systems. This methodology aligns with key principles of ethical AI development and responsible AI use, helping organizations mitigate unintended consequences and maintain robust AI systems.
Key Points:
-
Cross-functional collaboration ensures diverse perspectives and accountability across governance decisions
-
Policy automation enables scalable and consistent governance enforcement without manual bottlenecks
-
Risk-based approaches prioritize high-impact areas while enabling streamlined approval for low-risk AI initiatives
Transition: These strategic approaches provide the framework for detailed implementation methodologies that translate governance strategy into operational reality.

Detailed Implementation Methodologies
Building on strategic approaches, organizations need specific implementation methodologies that provide step-by-step guidance for operationalizing AI governance while addressing the practical challenges of scaling responsible AI practices across enterprise environments.
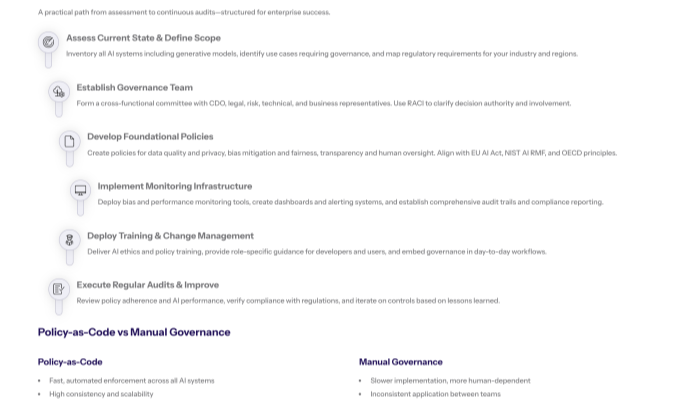
Step-by-Step: Phased Governance Implementation
When to use this: For organizations implementing AI governance from scratch or conducting major overhauls of existing governance programs to ensure comprehensive coverage and sustainable adoption.
-
Assess Current State and Define Scope: Conduct comprehensive inventory of existing AI technologies, including generative AI and machine learning models, use cases requiring governance oversight, regulatory requirements applicable to your industry, and current governance capabilities to establish baseline and identify implementation priorities.
-
Establish Governance Team: Form cross-functional governance committee including CDO, legal counsel, risk management leaders, and technical leads using RACI matrix to define decision-making authority, consultation requirements, and information distribution for all AI governance decisions.
-
Develop Foundational Policies: Create comprehensive AI governance policy covering data quality requirements, bias mitigation standards, transparency mandates, human oversight protocols, and compliance requirements aligned with relevant regulations like EU AI Act and industry standards. These policies should incorporate ethical guidelines and ethical considerations to promote ethical AI development and responsible AI use.
-
Implement Monitoring Infrastructure: Deploy automated tools for continuous oversight including bias detection systems, performance monitoring dashboards, audit trail capabilities, and compliance reporting mechanisms that provide real-time visibility into AI system behavior and governance adherence. Ensure that AI tools are capable of monitoring AI systems for data integrity, AI decisions, and AI outputs to mitigate AI related risks effectively.
-
Deploy Training Programs: Execute organization-wide change management initiatives including AI ethics training, policy communication, role-specific guidance for AI developers and users, and governance process training that builds capability for responsible AI practices across teams.
-
Execute Regular Audits: Establish ongoing review processes including policy adherence assessments, AI system performance evaluations, compliance verification against regulatory requirements, and continuous improvement initiatives that adapt governance based on operational experience and evolving regulations.
Comparison: Policy-as-Code vs. Manual Governance Implementation
Feature |
Policy-as-Code |
Manual Governance |
|---|---|---|
Implementation Speed |
Rapid deployment through automation |
Slower rollout requiring manual processes |
Consistency |
Uniform policy enforcement across all AI systems |
Variable application dependent on human judgment |
Scalability |
High scalability supporting enterprise AI adoption |
Limited scalability constrained by manual capacity |
Discover how artificial intelligence is reshaping audit capabilities |
Real-time audit trails with automated compliance reporting |
Periodic audit reports requiring manual documentation |
Adaptability |
Quick policy updates through configuration changes |
Slow adaptation requiring process retraining |
Resource Requirements |
Higher initial investment, lower ongoing operational costs |
Lower initial costs, higher ongoing manual effort |
Policy-as-Code accelerates implementation and ensures consistent enforcement while providing superior audit capabilities, making it ideal for organizations with significant AI adoption plans, while manual approaches offer flexibility for organizations with limited AI usage or unique governance requirements that resist automation.
Transition: Understanding these methodologies helps address the common challenges organizations face during governance implementation.

Common Challenges and Solutions
Organizations implementing AI governance face predictable obstacles that can derail implementation efforts or create governance gaps that expose the organization to AI risks and regulatory compliance failures.
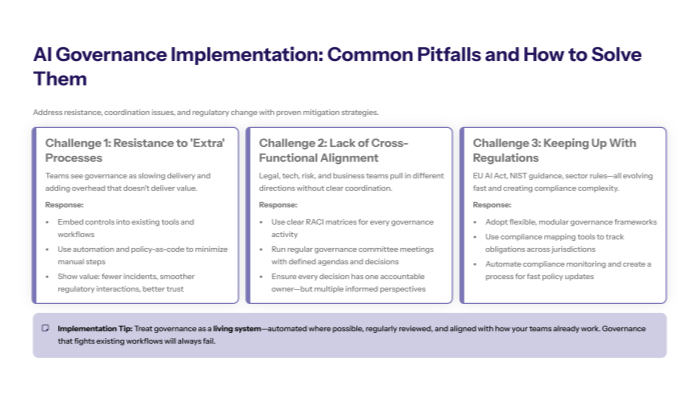
Challenge 1: Resistance to Governance Overhead
Solution: Embed AI governance into existing workflows using automation and streamlined processes that reduce manual burden while maintaining effective oversight and compliance.
Implement policy-as-code frameworks that automatically enforce governance requirements without requiring additional manual steps from AI developers, and demonstrate governance value by quantifying incidents prevented and regulatory compliance achieved through structured governance practices.
Challenge 2: Lack of Cross-Functional Alignment
Solution: Establish clear RACI matrices and regular governance committee meetings with defined decision-making authority that prevents governance paralysis while ensuring appropriate stakeholder input.
Include diverse perspectives from legal, technical, business, and ethics teams in governance decisions while maintaining clear accountability for outcomes, and create escalation paths that resolve conflicts efficiently without compromising governance effectiveness or slowing AI initiatives.
Challenge 3: Keeping Pace with Evolving Regulations
Solution: Implement flexible AI governance frameworks that adapt to evolving regulations like EU AI Act updates and emerging industry standards through modular policy structures and compliance mapping tools.
Use automated compliance monitoring that tracks regulatory changes and identifies required policy updates, ensuring governance frameworks remain current with regulatory requirements while minimizing manual effort to maintain compliance across multiple jurisdictions and standards.
Transition: Addressing these challenges enables sustainable governance implementation that supports long-term AI adoption goals.

Conclusion and Next Steps
Successful AI governance implementation requires structured approaches that combine organizational structures, policy frameworks, and technical controls to enable responsible AI practices while supporting business objectives and regulatory compliance. The best approaches integrate cross-functional collaboration, policy automation, and risk-based methodologies to create scalable governance that evolves with AI adoption and regulatory requirements.
By embedding ethical AI practices, ethical guidelines, and ethical AI development principles into your governance program, you ensure that AI systems operate fairly, transparently, and accountably. This approach mitigates AI related risks and unintended consequences, building stakeholder trust and enabling your organization to harness the full potential of artificial intelligence technologies, including generative AI and advanced machine learning models.
To get started:
-
Conduct governance readiness assessment to identify current state capabilities, governance gaps, and implementation priorities based on your AI adoption plans and regulatory environment
-
Establish cross-functional governance team with defined roles using RACI matrices, regular meeting schedules, and clear decision-making authority for AI governance matters
-
Select and pilot governance tools that support your chosen implementation approach, whether policy-as-code automation, manual processes, or hybrid methodologies aligned with organizational maturity
Related Topics: Explore AI risk management frameworks for deeper risk assessment methodologies, compliance automation tools for regulatory alignment, and governance maturity models for long-term capability development planning.


Additional Resources
Implementation Templates:
-
AI governance framework templates with policy examples addressing data quality, bias mitigation, and transparency requirements
-
RACI matrix examples for AI governance roles including legal, technical, business, and ethics stakeholders
-
Governance committee charter templates with meeting structures and decision-making processes
Compliance Resources:
-
EU AI Act compliance mapping guides with implementation timelines and requirements by AI system risk category
-
NIST AI Risk Management Framework implementation guidance with risk assessment templates and mitigation strategies
-
ISO/IEC 42001 alignment frameworks for AI management system certification and continuous improvement
Tool Evaluation Frameworks:
-
Governance platform evaluation criteria covering policy automation, monitoring capabilities, and compliance reporting
-
Vendor comparison frameworks for AI governance tools with feature analysis and implementation considerations
-
ROI calculation templates for governance program investment and value demonstration to stakeholders

