Enterprise AI Implementation Challenges: Overcoming Common Barriers
Introduction: Navigating the AI Landscape in the Business World
Enterprise AI implementation challenges are preventing 95% of organizations from achieving meaningful returns on their AI investments, despite the US alone crossing $40 billion in generative AI (gen AI) spending. While 81% of large organizations plan AI adoption within the next 12 months, most organizations struggle to translate AI initiatives beyond pilot stages into enterprise-wide value creation. MIT research reveals what experts call the “GenAI Divide”—a fundamental gap between massive AI investment and actual business value delivery.
AI presents unprecedented opportunities but also significant challenges. Implementation fails not because AI technologies lack capability, but because organizations treat AI as plug-and-play solutions rather than comprehensive business transformations requiring a mindset shift and a holistic approach.
What This Guide Covers
This guide examines the most critical technical, organizational, and strategic barriers preventing successful enterprise AI adoption, plus proven solutions from organizations achieving real AI success and business impact. We focus on actionable strategies for implementing AI and integrating AI systems into existing workflows rather than theoretical frameworks.
Who This Is For
This guide is designed for IT leaders, executives, and AI project managers in enterprise organizations. Whether you’re launching your first AI project or scaling existing AI initiatives across business processes, you’ll find specific strategies to overcome common implementation barriers, mitigate AI risks, and align AI efforts with business objectives.
Why This Matters
AI investment has surged 2.5 times since 2023, yet only one in four AI initiatives deliver expected ROI, and fewer than 20% achieve enterprise-wide scaling. Organizations that successfully navigate implementation challenges can expect $1 to $1.5 billion in business impact, while those that fail face expensive technology investments with no tangible outcomes.
What You’ll Learn:
Why data quality issues affect 73% of implementations and delay projects by six months
How to address the AI talent shortage impacting 68% of organizations through developing technical expertise and organizational readiness
Strategic approaches to cost management, including hidden costs and financial justification challenges
Proven frameworks for regulatory compliance, intellectual property infringement concerns, and risk mitigation
Infrastructure modernization requirements for scaling AI initiatives and integrating agentic AI systems
Step-by-step implementation methodologies from successful enterprise deployments, focusing on new workflows enabled by AI agents


Understanding Enterprise AI Implementation Fundamentals and AI Strategy
Enterprise AI implementation transforms organizational workflows through systematic integration of artificial intelligence across business processes, distinct from isolated pilot projects or standalone AI tools.
Most companies currently operate in what researchers term the “pilot trap”—88% use AI in at least one function, but only 33% achieve scaling beyond proof-of-concept stages. This gap exists because implementation requires fundamental changes to data infrastructure, governance frameworks, and organizational culture that pilot projects don’t address. AI continues to evolve rapidly, and organizations must keep pace with the shifting AI landscape and industry standards.
Implementation differs from simple AI adoption because it demands integration with existing systems, compliance with regulatory frameworks, and alignment with business objectives rather than just technical functionality.
The Implementation Maturity Spectrum and Using AI Effectively
Pilot Phase: Organizations test AI capabilities in controlled environments with simplified workflows and limited users. Nearly half of enterprises remain stuck at this stage because pilots don’t address real-world integration complexity, legacy infrastructure constraints, or enterprise-wide governance requirements.
Scaling Phase: Successful transition requires security reviews, formal change management processes, staff training, and systems integration. This phase typically demands 3-5 times more organizational effort than the initial pilot investment.
Enterprise-Wide Integration: Only 5% of enterprises reach this level, where AI systems—including agentic AI systems and AI agents—become integral to core business processes, delivering measurable efficiency gains, cost savings, and revenue growth. Organizations achieving this stage report transformative business value rather than incremental improvements.
Core Implementation Pillars for AI Success
Data Foundation: High-quality, accessible data across enterprise systems enabling AI models to generate valuable insights rather than fragmented outputs. Organizations struggle when 42% of business leaders report insufficient proprietary data for effective model customization.
Technical Infrastructure: Scalable systems capable of supporting AI workloads, with 86% of CIOs reporting unprepared network capacity. This includes integration capabilities bridging AI systems with legacy infrastructure without operational disruption, strict access controls to protect sensitive data, and compliance with regulatory frameworks.
Organizational Readiness and Technical Expertise: Cultural preparation through change management, upskilling programs, and governance frameworks. Without this foundation, even technically successful AI projects fail during operationalization phases. Developing internal technical expertise and fostering a culture ready for AI-driven transformation is a significant challenge but essential for long-term AI success.
Transition: Understanding these fundamentals reveals why specific implementation challenges create compounding barriers for enterprise AI success and highlights the need for a holistic approach.


The Top 8 Enterprise AI Implementation Challenges and How to Mitigate AI Risks
Organizations face interconnected barriers that compound implementation complexity and prevent AI initiatives from delivering business value. These challenges operate across technical, organizational, and strategic dimensions, creating what MIT researchers identify as systematic execution gaps rather than technology limitations.
When multiple challenges converge—such as data quality issues combined with skills gaps and infrastructure limitations—implementation complexity increases exponentially, explaining why 95% of companies see no real ROI from generative artificial intelligence investments.
1. Data Quality and Bias Issues (73% of Organizations)
Inaccurate training data leads to unreliable AI outputs that undermine decision making and create compliance risks. Organizations report data quality challenges delay projects by six or more months, making this the most frequently cited implementation barrier.
The challenge manifests in several critical ways. Historical bias perpetuation occurs when AI models trained on flawed datasets reproduce discriminatory patterns in hiring, lending, or customer service decisions. Many organizations discover their data contains systematic biases only after deploying AI systems in production, creating legal and reputational risks.
Data fragmentation across enterprise systems prevents AI models from accessing comprehensive information needed for accurate insights. When data exists in multiple formats and locations without unified access, AI capabilities remain limited to narrow use cases rather than enterprise-wide business processes.
2. Insufficient Proprietary Data for Model Customization (42%)
Organizations lack domain-specific datasets necessary for training AI models that deliver competitive advantage rather than generic capabilities. This challenge becomes especially acute for companies attempting to deploy specialized AI agents or fine-tune generative AI for industry-specific applications.
Without years of consistent data collection and curation, AI initiatives stall due to shallow data pools that cannot support meaningful model training. Organizations frequently underestimate the data requirements for effective AI customization, expecting immediate results from limited historical datasets.
The competitive implications are significant—companies with robust proprietary data can create differentiated AI capabilities, while those relying on generic models struggle to outpace competitors using similar publicly available AI tools.
3. Inadequate AI Expertise and Skills Gap (68%)
The shortage of qualified AI engineers, data scientists, and ML specialists directly impacts project scope and timeline, with 40% of enterprises lacking adequate AI expertise to meet organizational goals. This creates dangerous single points of failure where key personnel departures can collapse entire initiatives.
Existing workforce AI literacy gaps compound the problem—only 28% of employees know how to use their company’s AI applications, despite enterprises running an average of 200 AI tools. This reveals massive training and organizational readiness shortfalls.
Competition for top AI talent drives hiring costs beyond many organizations’ budgets, while the rapid evolution of AI technologies means even experienced professionals struggle with emerging frameworks and model architectures. Organizations often find themselves simultaneously competing for scarce external talent while inadequately preparing internal teams for AI adoption.
4. Financial Justification and ROI Challenges (42%)
Organizations struggle to quantify AI business value and secure ongoing stakeholder support when benefits remain vague or long-term. High upfront costs for infrastructure, talent, and training create budget approval obstacles, especially when leadership cannot model clear returns on investment.
The measurement challenge operates on two levels. First, organizations often track AI model accuracy rather than business impact, creating a gap between technical success and financial value. Second, long payback periods make AI initiatives vulnerable to budget cuts when economic conditions tighten.
Successful financial justification requires aligning AI initiatives with specific KPIs, demonstrating quick wins that build confidence, and explicitly modeling ROI for stakeholder communication rather than relying on general productivity claims.
5. Privacy, Security Concerns, and Intellectual Property Infringement
AI systems introduce new risks around sensitive data, security concerns, and regulatory compliance that organizations must navigate while maintaining operational efficiency. Regulatory frameworks like GDPR and CCPA create strict requirements for AI processing of personally identifiable information, with non-compliance carrying significant financial penalties.
Data security vulnerabilities emerge when AI models require access to enterprise data across systems, creating broader attack surfaces. Organizations worry about intellectual property infringement when using generative AI systems that may inadvertently reproduce copyrighted materials in their outputs.
Industry-specific compliance requirements add complexity—healthcare, financial services, and government organizations face additional regulatory scrutiny for AI implementations affecting critical decisions or sensitive data.
6. Infrastructure and Integration Limitations in the Physical World
Legacy infrastructure creates scaling bottlenecks that prevent AI initiatives from reaching enterprise-wide adoption. When 86% of CIOs report unprepared network capacity for AI workloads, technical constraints become fundamental barriers to implementation success.
Integration complexity escalates when every new AI use case requires manual connections to fragmented systems. Poor integration produces cascading problems: inconsistent data across platforms, fragmented AI insights that fail to inform business processes, and operational inefficiencies that undermine intended AI benefits.
Many organizations discover their existing systems lack the processing capacity for AI model demands or real-time performance capabilities required by modern AI agents, necessitating significant infrastructure investments before AI implementation can proceed.
7. Treating AI Projects as Isolated Experiments Instead of Strategic Initiatives
Organizations often treat AI projects as isolated technology experiments without embedding them into broader business objectives or new workflows. This approach leads to fragmented efforts, lack of leadership ownership, and failure to realize enterprise-wide benefits.
AI continues gaining traction as a transformative force, but only organizations that adopt a strategic AI strategy and integrate AI holistically across functions realize sustainable success.
8. Lack of Comprehensive Risk Mitigation and Governance Frameworks
Without robust AI governance frameworks, organizations expose themselves to risks including model drift, bias, security breaches, and regulatory non-compliance. Mitigating AI risks requires continuous monitoring, strict access controls, and clear accountability structures.
Successful enterprises embed AI risk management into their operational processes, ensuring ongoing evaluation of AI system performance and alignment with evolving industry standards.


Strategic Solutions and Implementation Framework for AI Success
Organizations achieving AI success implement systematic approaches that address interconnected challenges through coordinated strategies rather than isolated technical solutions. High-performing organizations recognize that AI implementation represents organizational transformation requiring comprehensive planning, stakeholder alignment, and phased execution.
The most successful enterprises adopt portfolio approaches, treating AI as an ongoing effort rather than discrete projects, and establish governance frameworks before scaling beyond pilot stages.
Step-by-Step: Building AI Implementation Readiness and Using AI to Achieve Business Objectives
When to use this framework: Organizations moving from pilot projects to scaled enterprise AI deployment across multiple business processes.
Conduct Comprehensive Data Audit: Assess data quality, accessibility, and coverage across enterprise systems. Identify gaps preventing effective AI model training and establish data governance protocols with automated validation systems.
Establish AI Governance Framework: Implement compliance protocols addressing regulatory requirements, risk mitigation strategies, and ethical concerns. Create AI lifecycle management processes with defined checkpoints from development through production monitoring.
Develop Talent Strategy: Launch upskilling programs for existing workforce while identifying critical external hiring needs. Establish partnerships with educational institutions or AI vendors to address expertise gaps without over-reliance on limited internal experts.
Create Infrastructure Modernization Plan: Assess network capacity, storage requirements, and integration capabilities for AI workloads. Develop phased upgrade strategy prioritizing systems supporting highest-impact AI use cases first.
Implement Portfolio Management: Establish measurable KPIs aligned with business objectives, create clear success metrics for each AI initiative, and implement regular review processes ensuring projects deliver tangible business value rather than just technical achievements.
Integrate AI Across Workflows: Redesign business processes to incorporate AI agents and agentic AI systems effectively, enabling new workflows that maximize AI capabilities and cost savings.
Mitigate AI Risks Continuously: Embed risk management protocols including bias detection, security monitoring, and intellectual property safeguards throughout the AI lifecycle.
Comparison: In-House vs. Partner-Assisted Implementation
Criteria |
In-House Development |
Partner-Assisted Implementation |
|---|---|---|
Development Speed |
12-18 months for enterprise scaling |
6-12 months with proven frameworks |
Customization Control |
Full control over AI capabilities |
Limited to partner platform capabilities |
Long-term Costs |
Lower ongoing costs after initial investment |
Higher ongoing licensing and service fees |
Technical Expertise |
Requires significant internal hiring |
Leverages external specialized knowledge |
Risk Management |
Full responsibility for compliance and security |
Shared responsibility with proven protocols |
Organizations with strong technical teams and unique requirements benefit from in-house development, while companies needing faster implementation or lacking AI expertise achieve better results through strategic partnerships that provide immediate access to proven frameworks and specialized knowledge.


Common Implementation Pitfalls and Proven Solutions to Mitigate AI Risks
Enterprise AI initiatives fail predictably when organizations repeat preventable mistakes that successful companies have already solved. These pitfalls represent systematic execution gaps rather than technology limitations, meaning proper planning and organizational readiness can eliminate most implementation barriers.
Challenge: Treating AI as Plug-and-Play Technology
Solution: Implement comprehensive change management programs that prepare organizational culture for AI-driven workflow transformation.
Organizations expecting immediate productivity gains from AI tools without workflow redesign inevitably face adoption resistance and limited business impact. Successful implementation requires treating AI as business process transformation, involving affected employees in design decisions, and providing extensive training on new AI-enhanced workflows rather than simply providing access to AI technologies.
Challenge: Underestimating Data Governance Requirements
Solution: Establish centralized data quality frameworks with automated validation systems and real-time monitoring capabilities.
Many organizations deploy AI models using inconsistent or fragmented data, leading to unreliable outputs and compliance risks. Successful enterprises implement federated learning approaches enabling AI model training across distributed systems while maintaining data residency requirements, plus synthetic data generation strategies for augmenting limited proprietary datasets.
Challenge: Scaling Beyond Proof-of-Concept Stage
Solution: Adopt portfolio management approaches with clear success metrics, executive sponsorship, and systematic resource allocation across multiple AI initiatives.
The pilot-to-production gap destroys most AI initiatives when organizations fail to address integration complexity, governance requirements, and organizational change management. Companies like Johnson & Johnson successfully manage 900+ AI projects by recognizing that 80% of business value comes from 10-15% of initiatives, enabling focused investment in highest-impact use cases while maintaining experimental approaches for emerging opportunities.
Challenge: Inadequate Risk Mitigation Planning
Solution: Implement comprehensive AI risk management protocols including model performance monitoring, bias detection systems, and continuous compliance validation.
Organizations deploying AI systems without ongoing monitoring face model drift, compliance failures, and security vulnerabilities that undermine business value and create legal risks. Successful implementation requires establishing measurement frameworks tracking AI model performance continuously, automated alerts for performance degradation, and systematic retraining processes maintaining AI system effectiveness over time.


Conclusion and Next Steps: Embracing AI Strategy for Long-Term Success
Enterprise AI implementation success requires systematic approaches addressing interconnected challenges rather than technology-first strategies that ignore organizational readiness. Organizations achieving meaningful business value recognize that artificial intelligence presents transformation opportunities demanding comprehensive planning, stakeholder alignment, and disciplined execution across technical and cultural dimensions.
The path forward emphasizes proactive challenge mitigation over reactive problem-solving, with successful enterprises investing in data governance, talent development, and change management before scaling AI capabilities across business processes.
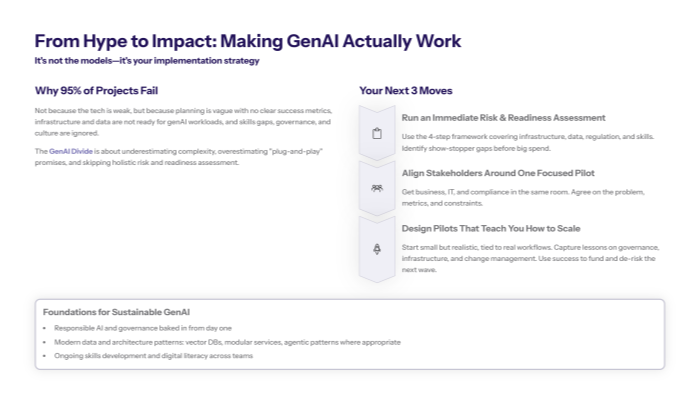
To get started:
Conduct AI readiness assessment: Evaluate current data quality, technical infrastructure, and organizational capability against implementation requirements for highest-priority AI use cases.
Establish cross-functional implementation team: Create dedicated AI governance structure with executive sponsorship, technical expertise, and business process ownership ensuring comprehensive challenge mitigation.
Develop phased implementation roadmap: Design systematic scaling approach with clear success metrics, risk mitigation protocols, and resource allocation strategies based on proven enterprise frameworks.
Related Topics: AI governance frameworks for regulatory compliance, data modernization strategies enabling effective AI model training, and enterprise change management approaches preparing organizational culture for AI-driven transformation.

