Operationalizing AI Governance Frameworks Across Teams
AI governance framework implementation transforms governance policies into operational systems that actively manage AI related risks and ensure regulatory compliance across your organization’s artificial intelligence initiatives. Unlike selecting frameworks or drafting policies, implementation involves deploying technical controls, establishing continuous monitoring systems, and integrating governance practices into daily AI operations. This practical process has become essential as organizations face evolving regulations like the EU AI Act and need to demonstrate trustworthy AI through measurable compliance.
This guide addresses the critical gap between having an AI governance framework on paper and establishing a robust AI governance framework that actively manages how AI systems operate throughout the AI lifecycle.
What This Guide Covers
This guide focuses exclusively on implementation processes, deployment methodologies, and practical integration steps for operationalizing AI governance frameworks. We cover technical infrastructure setup, organizational integration strategies, and structured rollout approaches—not framework comparison or theoretical governance concepts. Emphasis is placed on ethical considerations, data privacy, and using AI tools to mitigate bias and improve AI outcomes.
Who This Is For
This guide is designed for CIOs, Chief Data Officers, AI program managers, AI developers, compliance teams, and technology leaders responsible for operationalizing AI governance. Whether you’re facing regulatory compliance deadlines or need to scale responsible AI practices across multiple AI applications, you’ll find actionable governance strategies and best practices.
Why This Matters
Moving from governance framework selection to actual implementation directly impacts regulatory compliance, operational risk mitigation, and the ethical development of AI systems. Organizations must demonstrate working governance systems rather than policy documents as AI regulations tighten and stakeholder expectations for responsible AI usage increase.
What You’ll Learn:
-
Implementation planning and readiness assessment strategies that align with ethical AI practices and safety AI systems
-
Framework-specific deployment methodologies for NIST AI Risk Management Framework and EU AI Act compliance
-
Technical infrastructure requirements and organizational integration approaches supporting continuous monitoring and data privacy
-
Step-by-step rollout processes with risk-based prioritization to optimize AI development and model development lifecycles


Understanding AI Governance Framework Implementation and Risk Management Frameworks
AI governance framework implementation is the systematic process of operationalizing governance policies into working technical and organizational systems that actively manage AI related risks and ensure compliance throughout AI development and deployment.
Implementation differs fundamentally from framework selection or policy creation because it requires establishing measurable controls, automated monitoring systems, and integrated workflows that function within existing organizational structures. While governance frameworks provide guidelines and policies establish intentions, implementation creates the actual mechanisms that govern how AI systems operate in practice.
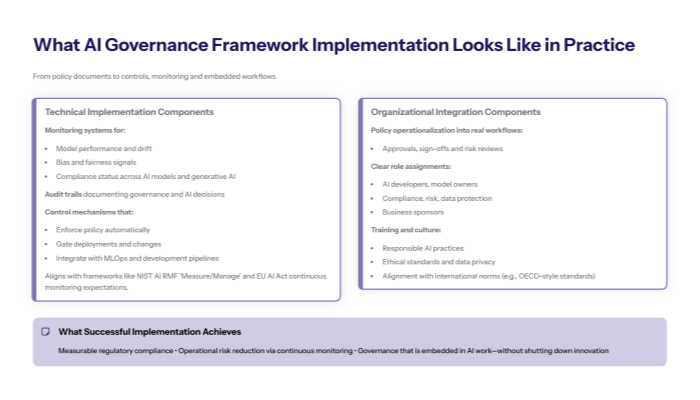
Successful implementation achieves three critical outcomes: measurable compliance with applicable regulatory frameworks, operational risk reduction through continuous monitoring, and seamless integration of governance practices into AI development workflows without inhibiting innovation.
Core Implementation Components: Integrating AI Tools and Ethical Standards
Technical infrastructure setup forms the foundation of effective AI governance framework implementation, requiring monitoring systems that track AI system performance, audit trails that document governance decisions and AI decisions, and control mechanisms that enforce compliance automatically. Organizations must deploy AI tools that detect risks such as bias, performance degradation, or non-compliance across their AI models and generative AI applications.
This connects to governance framework implementation because technical setup must align with chosen framework requirements—whether implementing the NIST AI Risk Management Framework’s “Measure” function or establishing continuous monitoring for EU AI Act compliance. Incorporating training data quality assessments and model development checkpoints ensures ethical standards are upheld throughout the AI lifecycle.
Organizational Integration Elements: Embedding Ethical Development and Governance Strategies
Building on technical components, organizational integration ensures governance becomes part of daily operations through policy operationalization, clear role assignments, comprehensive training programs, and workflow integration. This involves establishing roles and accountabilities for AI developers, approval, monitoring, and remediation while ensuring cross-functional collaboration between legal, technical, and business units.
Beyond technical setup, organizational integration embeds ethical principles and responsible AI practices into company culture, transforming governance from compliance burden into core organizational value that supports both innovation and risk management. Aligning AI governance policies with international economic co operation standards further strengthens compliance efforts.
Transition: Understanding these foundational components enables organizations to select the most appropriate implementation approach based on their specific risk profile, regulatory environment, and operational constraints.

Implementation Approaches and Methodologies for Responsible AI and Regulatory Compliance
Different organizations require different strategic approaches to AI governance framework implementation, depending on their AI adoption maturity, regulatory pressures, and resource constraints. The choice of implementation methodology significantly impacts timeline, resource allocation, and ultimate success of governance program deployment.
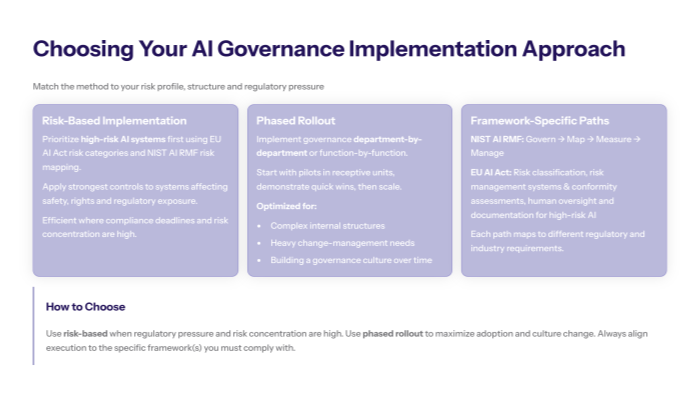
Risk-Based Implementation Strategy Aligned with AI Act and NIST AI Risk Management
Risk-based implementation prioritizes high-risk AI systems first, using EU AI Act classifications or NIST risk categories to determine deployment sequence. Organizations assess AI applications based on potential impact on safety, fundamental rights, and regulatory requirements, implementing comprehensive governance controls for high-risk AI systems while applying proportionate measures for lower-risk applications.
This approach allocates resources efficiently by focusing on AI systems that pose the greatest potential harm or regulatory exposure, ensuring compliance with evolving regulations while managing implementation costs and organizational disruption. It also supports mitigating bias and improving AI outcomes through targeted interventions.
Phased Rollout Methodology for Sustainable Ethical AI Practices
Phased rollout methodology focuses on organizational readiness rather than system risk levels, implementing governance frameworks department-by-department or function-by-function to ensure adequate training, change management, and cultural integration at each stage. Organizations begin with pilot programs in receptive departments, demonstrate early wins, and gradually scale governance practices across the entire organization.
Unlike risk-based approaches, this methodology emphasizes stakeholder buy-in and sustainable adoption over immediate risk reduction, making it suitable for organizations with complex internal structures or significant change management challenges. It fosters ethical development and continuous improvement in AI governance practices.
Framework-Specific Implementation Paths for Trustworthy AI
Different governance frameworks require distinct implementation approaches. NIST AI RMF implementation follows the four core functions—Govern, Map, Measure, and Manage—requiring organizations to establish governance policies, understand AI system contexts, continuously monitor performance, and allocate resources for risk mitigation. EU AI Act compliance pathways focus on conformity assessments, risk management systems, and human oversight requirements for high-risk AI systems.
Key Points:
-
Risk-based prioritization addresses regulatory compliance urgency and safety AI systems
-
Phased rollouts ensure sustainable organizational adoption and embedding of ethical standards
-
Framework-specific paths align implementation with regulatory requirements and data privacy mandates
Transition: Regardless of chosen approach, successful implementation requires following structured processes that address both technical and organizational requirements systematically.

Step-by-Step Implementation Process with Emphasis on AI Governance Policies and AI Security
Effective AI governance framework implementation requires systematic execution that builds organizational capability while establishing technical controls. The following process integrates technical infrastructure development with organizational change management to ensure governance frameworks become operational rather than aspirational.
Step-by-Step: Framework Implementation Deployment
When to use this: Organizations beginning formal AI governance framework implementation with defined regulatory requirements and stakeholder commitment.
-
Assessment and Readiness Planning: Conduct comprehensive inventory of existing AI systems, evaluate current governance practices against framework requirements, identify gaps in technical infrastructure and organizational capabilities, and establish implementation timeline with resource allocation plans. This includes assessing data privacy risks and AI security vulnerabilities.
-
Framework Customization: Adapt chosen governance framework to specific organizational context, industry requirements, and applicable regulatory frameworks, ensuring alignment with business objectives while maintaining compliance with relevant AI regulations, ethical guidelines, and governance strategies.
-
Infrastructure Setup: Deploy technical systems for continuous monitoring of AI models, establish audit trails and documentation systems, integrate governance controls with existing development workflows, and implement automated risk assessment tools throughout the AI lifecycle. Leverage AI tools designed for bias mitigation and model explainability to enhance transparency.
-
Training and Change Management: Educate staff on governance policies and procedures, establish clear roles and responsibilities for AI governance program management, integrate ethical considerations into AI development processes, and create feedback mechanisms for continuous improvement. Training data management and ethical AI practices are emphasized to ensure compliance.
-
Monitoring and Validation: Implement performance measurement systems for governance effectiveness, establish compliance verification processes, create escalation procedures for governance violations, and develop continuous improvement protocols based on monitoring results. Continuous monitoring ensures AI systems operate within ethical standards and regulatory boundaries.
Comparison: In-House vs Vendor-Supported Implementation
Feature |
In-House Implementation |
Vendor-Supported |
|---|---|---|
Timeline |
12-18 months |
6-12 months |
Cost |
Lower ongoing costs |
Higher initial investment |
Maximum flexibility |
Standard configurations | |
Ongoing Support |
Internal expertise required |
External expertise included |
Compliance Assurance |
Requires internal expertise |
Built-in regulatory knowledge |
Organizations with strong technical capabilities and unique requirements benefit from in-house implementation, while those facing tight regulatory deadlines or lacking specialized expertise should consider vendor-supported approaches for faster deployment and built-in compliance features.
Transition: Even with structured processes, organizations encounter predictable implementation challenges that require specific solutions and mitigation strategies.


Common Implementation Challenges and Solutions for Ethical Standards and AI Governance Important
Implementation journeys typically encounter obstacles related to organizational resistance, technical integration complexity, and regulatory compliance management. Addressing these challenges proactively prevents deployment delays and ensures sustainable governance framework adoption.
Challenge 1: Resistance to New Processes and Controls
Solution: Implement gradual deployment with clear communication of benefits, demonstrate early wins through pilot programs, and involve stakeholders in governance framework design to ensure buy-in across internal and external stakeholders.
Successful change management requires showing how governance frameworks enhance rather than hinder AI development, connecting responsible AI practices to business value creation and risk mitigation rather than presenting them as compliance burdens.
Challenge 2: Integration with Legacy Systems and Workflows
Solution: Use API-based integration approaches to connect governance tools with existing AI development platforms, implement phased migration strategies that maintain business continuity, and establish parallel system operation during transition periods to minimize disruption.
Technical integration challenges often involve connecting modern governance tools with established data management systems, requiring careful planning to ensure data quality and maintain operational efficiency during implementation.
Challenge 3: Maintaining Compliance Across Multiple Jurisdictions
Solution: Implement highest common standard approach that satisfies the most stringent applicable regulations, use compliance mapping tools to track requirements across jurisdictions, and establish regional adaptation processes for jurisdiction-specific requirements.
Organizations operating globally must navigate complex regulatory frameworks including OECD AI principles, various national AI regulations, and applicable data protection laws, requiring sophisticated compliance management strategies.
Transition: Successfully addressing these challenges positions organizations for sustainable governance framework operation and continuous improvement.


Conclusion and Next Steps for Responsible Development and AI Governance Practices
Successful AI governance framework implementation requires structured approach that integrates technical infrastructure with organizational capabilities, ensuring governance becomes operational rather than aspirational. Organizations must balance comprehensive governance with innovation enablement, establishing measurable controls without creating barriers to responsible AI development and deployment.
To get started:
-
Conduct implementation readiness assessment including AI system inventory, gap analysis, and resource planning emphasizing ethical standards and data privacy
-
Select pilot programs for initial deployment focusing on high-risk AI systems or receptive organizational units to demonstrate effective governance strategies
-
Establish project governance with clear timeline, stakeholder roles, and success metrics for governance framework rollout
Related Topics: AI risk management strategies support ongoing governance effectiveness, compliance monitoring tools enable continuous oversight, and organizational change management principles ensure sustainable governance adoption—all critical for maintaining governance framework effectiveness as AI technologies and regulatory requirements evolve.


Additional Resources
Implementation Checklists:
-
AI system inventory templates for governance scope definition
-
Gap analysis frameworks for readiness assessment
-
Stakeholder communication templates for change management
Vendor Evaluation Frameworks:
-
Governance platform comparison criteria
-
Integration capability assessment tools
-
Compliance feature verification checklists
Compliance Templates:
-
NIST AI RMF implementation guides
-
EU AI Act compliance documentation requirements
-
Risk assessment templates for various AI applications

